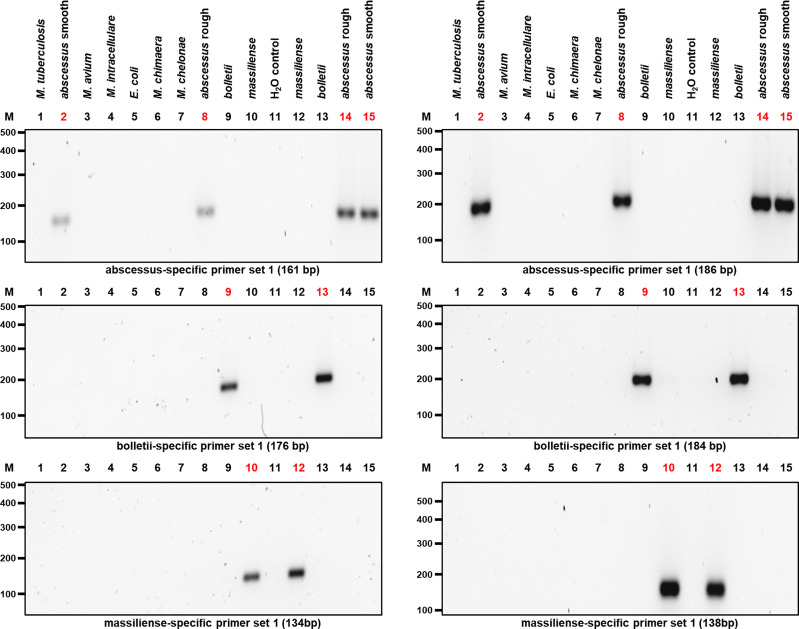
Figure 3.
PCR results after optimizing the amplification of the candidate genes used to isolate the three MABC subspecies. Two different sets of primers pairs as shown in Table 1 were used to differentiate MABC into its subspecies. M. abscessus (rough and smooth morphotypes), M. bolletii, M. massiliense and other bacterial species used as controls including M. chelonae, M. tuberculosis, M. avium, M. intracellulare, M. chimaera, and E. coli were selected. Both M. abscessus strains including rough and smooth morphotypes yielded 161-bp and 186-bp gene amplicons, respectively (Top Panel). In addition, M. bolletii yielded 176-bp and 184-bp gene amplicons, respectively (Middle Panel). Lastly, M. massiliense yielded 134-bp and 138-bp gene amplicons, respectively (Bottom Panel). Each MABC subspecies yielded an amplified PCR product that was specific to that species.