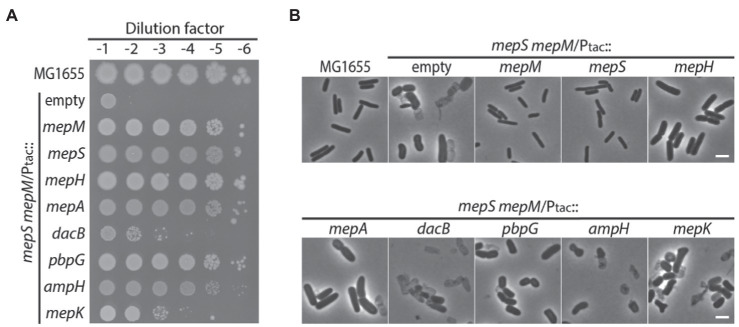
Figure 1.
DD-endopeptidases other than MepS, MepM, and MepH can also function in cell wall assembly. (A) Spot dilution assay on LB agar for MG1655 (wild type) and HC611 (Para::mepS, ΔmepM) strains harboring plasmids that overexpress various DD-endopeptidase genes: pHC800 (empty vector), pTK1(mepM), pTK2(mepS), pTK3(mepH), pTK4(mepA), pTKD1(dacB), pTKD4(pbpG), pTKD5(ampH), or pWJ20(mepK). The strains were grown overnight in M9-arabinose medium and normalized for cell density to an OD600 of 2. The normalized cultures were serially diluted 10-fold in LB and 5 μl of each dilution (10−1–10−6) was spotted onto LB agar lacking arabinose but containing 1 mM IPTG to deplete mepS expression and induce the expression of various DD-endopeptidases from the tac promoter. The plates were incubated at 30°C and photographed after 22 h. (B) Phase contrast images of the same strains after growth in LB. Overnight cultures were washed with LB and diluted to an OD600 of 0.01 in LB containing 1 mM IPTG. Growth was then continued at 37°C with agitation. After incubation for 4 h, samples of the cells were chemically fixed and the cells were imaged using phase contrast optics. The bars equal 3 μM.