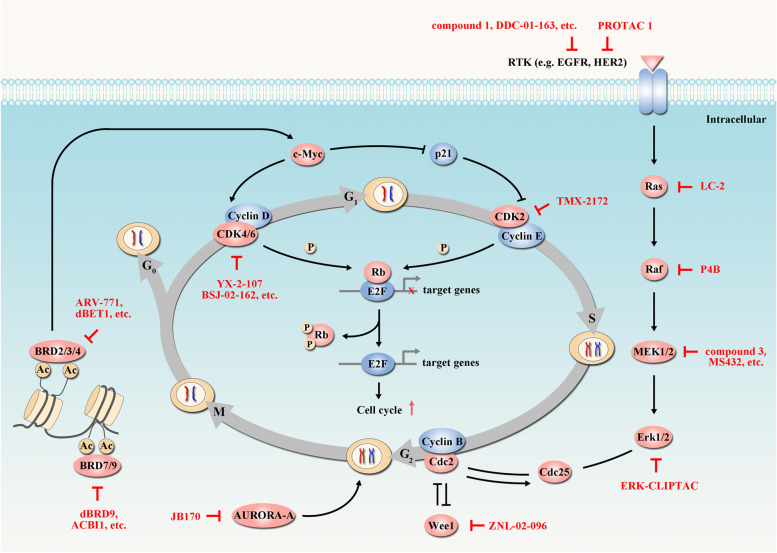
Fig. 3.
PROTACs targeting cancer proliferation. In cell cycle regulation, some proteins (e.g. c-Myc, p21) act as accelerator or inhibitor to regulate CDK expression. CDKs and their chaperones phosphorylate retinoblastoma protein (Rb), thus releasing transcription factor E2F and promoting DNA replication. The RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway also plays a central role in growth-promoting signaling and elicits cell cycle progression. These key elements in cancer proliferation can be targeted by diverse PROTACs (red arrow). Tumor-suppressor proteins are indicated in blue and oncogenic proteins are indicated in red. In the presented pathways, PROTACs have been developed targeting BRD4 [12, 76], CDK4/6 [77, 78], EGFR [79, 80], AURORA-A [81], Raf [60], BRD7/9 [82, 83], CDK2/5 [84], ERK1/2 [26], HER2 [79], MEK1/2 [85, 86], Ras [87] and Wee1 [88]