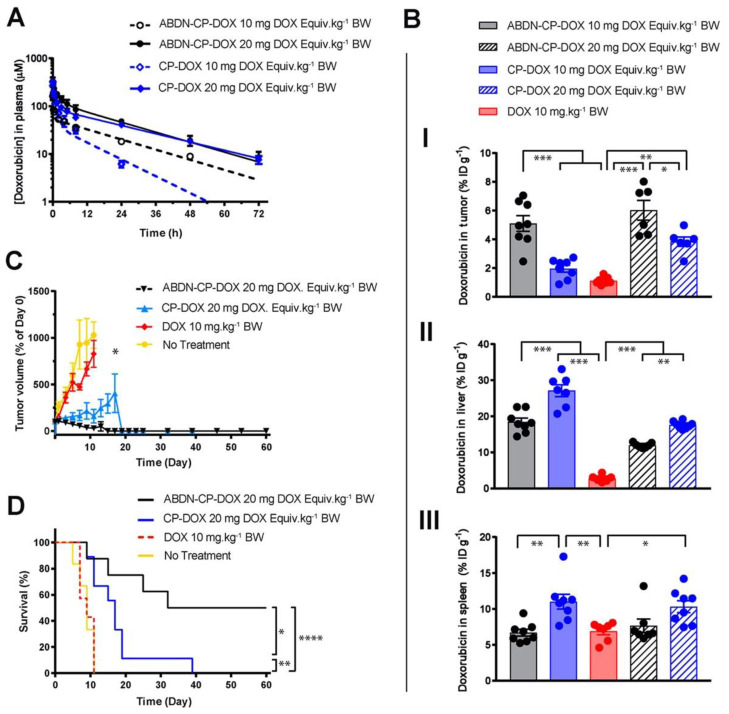
Figure 3.
Role of dosing on nanoparticle drug efficacy. An albumin binding nanoparticle of doxorubicin (ABDN-CP-DOX) was compared head-to-head with a non-albumin binding counterpart (CP-DOX). (A) pharmacokinetic profile of the nanoparticles at different doses in mice. (B) Biodistribution of the doxorubicin conjugated to various nanoparticles at 24 h post-administration in the (I) tumor, (II) liver, and (III) spleen. All nanoparticles show better tumor accumulation and less liver accumulation at the higher dose. (C) Tumor regression curve in an s.c. mouse C26 colon cancer model, up to day 60. (D) cumulative survival of tumor-bearing mice treated with indicated drugs. * for p < 0.05, ** for p < 0.01, *** for p < 0.001, and **** for p < 0.0001. Reprinted (adapted) with permission from [56]. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.