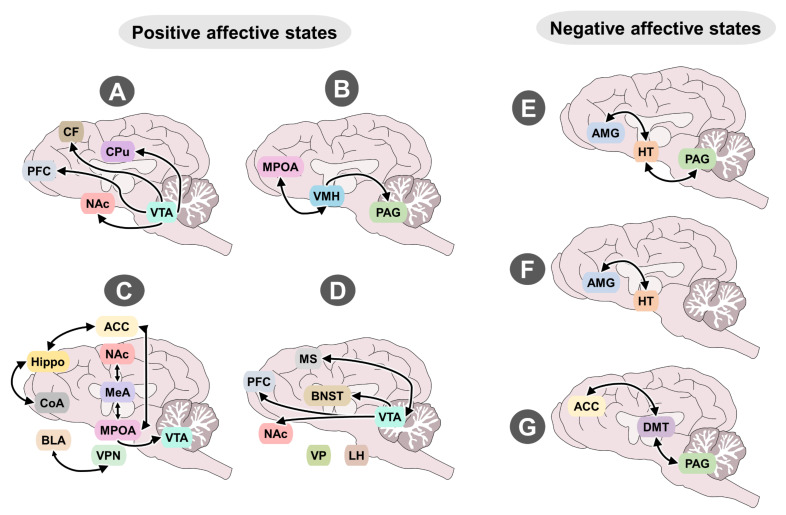
Figure 3.
The seven basic behavioral neurocircuits according to Panksepp [9], schematized in a sagittal section of a dog’s brain. On the left side are the systems that evoke positive affective states: (A) seeking; (B) lust; (C) care and (D) play. On the right are the ones that evoke negative affective states: (E) rage; (F) fear; and (G) panic. Numerous brain regions are involved in these systems: amygdala (AMG), hypothalamus (HT), periaqueductal gray matter (PAG), anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), dorsomedial thalamus (DMT), prefrontal cortex (PFC), frontal cortex (CF), nucleus accumbens (NAc), ventral tegmental area (VTA), caudal putamen (CPU), medial preoptic area (MPOA), ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), hippocampus (Hippo), cortical amygdala (CoA), basolateral (BLA), medial (MBA), and paraventricular nuclei (PVN), medial septum (MeA), bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), ventral pallidum (VP), and lateral hypothalamus (LH).