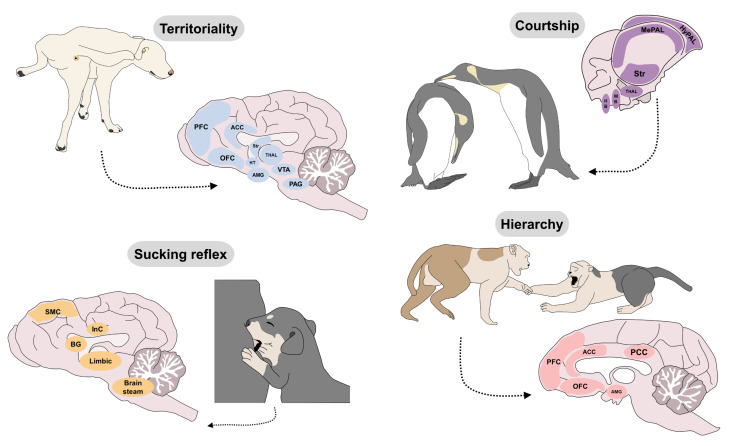
Figure 5.
The basic neurobiological systems of behavior evoke developmentally-dependent innate responses. For example, delimiting a territory by marking it with urine reflects the systematic activity of the rage/seeking/lust systems and begins at puberty. Courtship behavior, as in the case of the male penguin that sticks out its chest, raises its beak, and tilts its head back (lust/care systems). The suckling reflex in puppies (seeking, panic) and the establishment of dominance hierarchies in wolf packs (rage/seeking) are other examples. In every innate response, the main cerebral structures involved in the processing of its respective integration is schematized in the brain. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; AMG: amygdala; BG: basal ganglia; HB: hindbrain; HT: hypothalamus; HyPAL: hyperpallium; InC: insular cortex; MB: midbrain; MePAL: mesopallium; OFC: orbitofrontal cortex; PAG: periaqueductal gray; PCC: posterior cingulate cortex; PFC: prefrontal cortex; SMC: sensorimotor cortex; Str: striatum; THAL: thalamus; VTA: ventral teg-mental area.