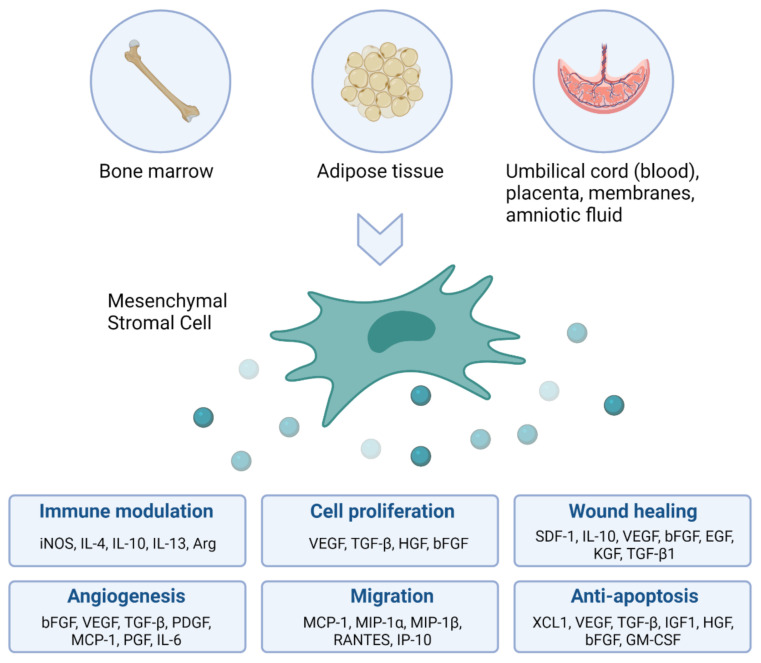
Figure 1.
The therapeutic function of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). MSCs can be isolated from a variety of tissue sources. Cultured MSCs have been used for several therapeutic purposes, both in experimental research and clinical applications. MSCs have the ability to modify their pleiotropic effects based on the in vivo environment they encounter. The secretome of MSCs is known to be involved in immune modulation, cell proliferation, wound healing, angiogenesis, migration and anti-apoptosis. Figure created with Biorender.com, accessed on 28 March 2022.