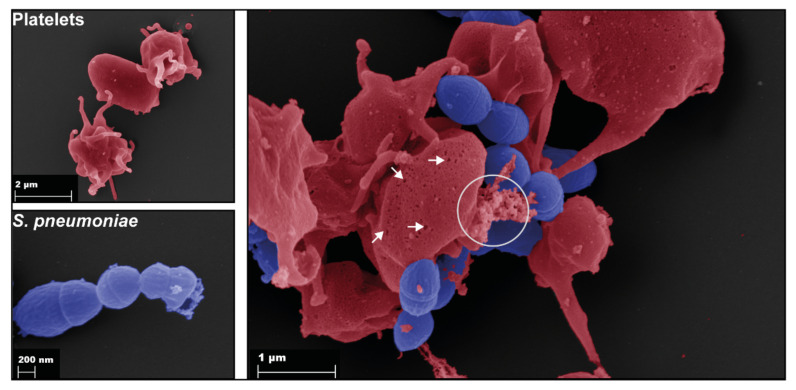
Figure 2.
Binding of S. pneumoniae (blue) to platelets (red). Scanning electron microscopy of single platelets (upper left), single pneumococci (bottom left), and platelets incubated with the pneumococcal TIGR4 strain for 1 h (right). The right image shows binding of pneumococci to platelets. In addition, pneumolysin pores are formed in platelet membranes (arrows), and released granule content is visible (circle).