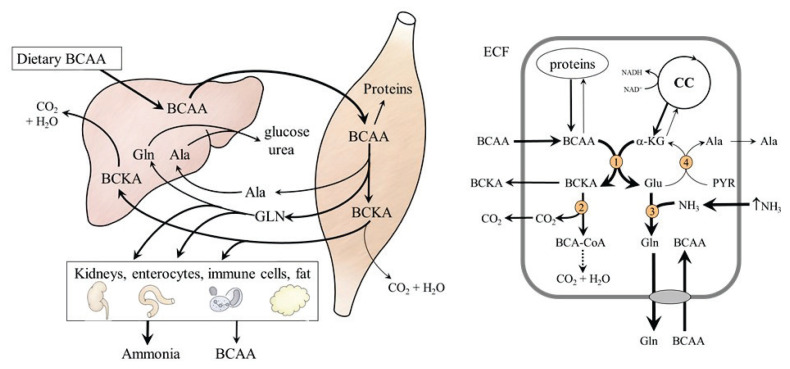
Fig. 3.
Effects of BCAA load on amino acid metabolism. On the left: BCAA administration leads to the release of GLN, alanine and BCKA from muscles. Glutamine is catabolized in visceral tissues to form ammonia. Part of the BCKA released from the muscles is used for BCAA synthesis. On the right: Effects of hyperammonaemia. Ammonia detoxification to GLN increases flux of BCAA through BCAA aminotransferase and the drain of α-KG from citric cycle. 1, BCAA aminotransferase; 2, BCKA dehydrogenase; 3, GLN synthetase; 4, alanine aminotransferase.