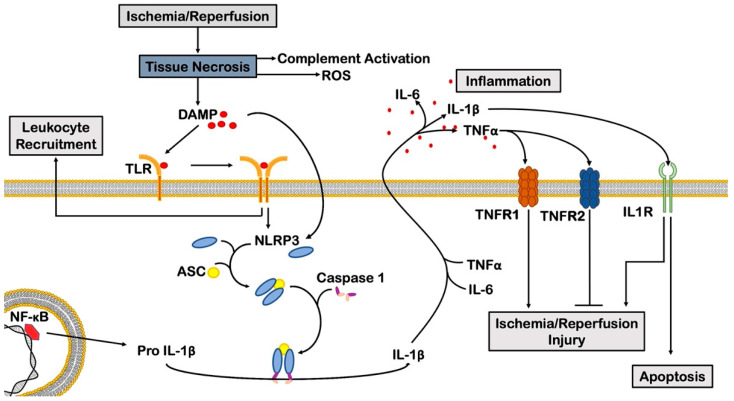
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the main signaling contributing to inflammation during myocardial ischemia. The inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines represents a useful therapeutic strategy to limit ischemic injury. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; IL, interleukin; IL1R, interleukin 1 receptor; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NLRP3, Nod-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain containing 3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF(R), tumor necrosis factor (receptor); TLR, Toll-like receptor.