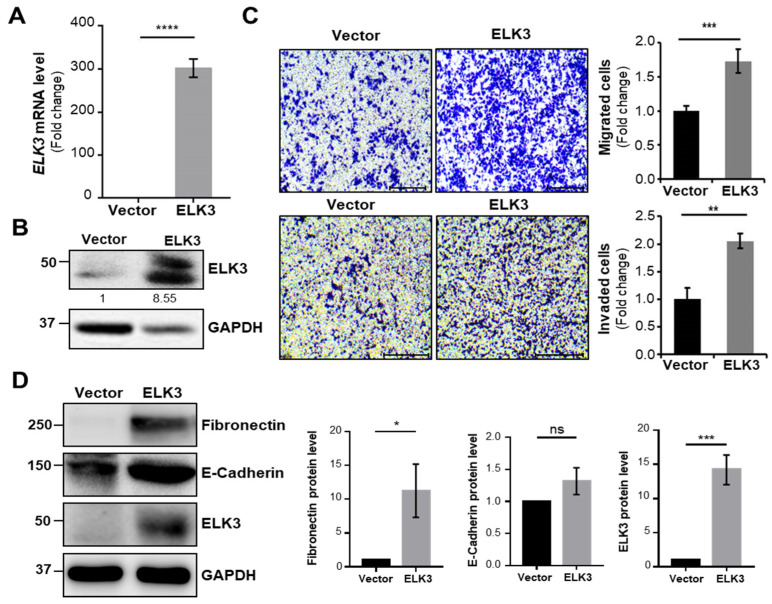
Figure 2.
ELK3 increases the migration and invasion of SNU484 cell line in E-cadherin independent manner. (A) ELK3 mRNA levels in SNU484 cells transfected with control vector and pLenti-cMyc-DDK-ELK3 plasmid. Error bars represent the standard deviation; **** p < 0.0001 (student’s t-test). (B) ELK3 protein levels in SNU484 cells transfected with control vector and pLenti-cMyc-DDK-ELK3 plasmid. The values indicate the signal intensities of ELK3 relative to GAPDH. (C) Representative images showing cell migration (top two panels) and cell invasion (bottom two panels) of SNU484 cells transfected with control vector and pLenti-cMyc-DDK-ELK3 plasmid. Scale bar, 200 μm. Bar graphs indicate the number of migrated cells and invaded cells. Error bars represent the standard deviation; ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 (student’s t-test). (D) Epithelial marker (E-cadherin), mesenchymal marker (Fibronectin), and ELK3 protein expression in SNU484 cells transfected with control vector and ELK3. Bar graphs indicate the quantified levels of each protein, in relative scales. Error bars represent the standard deviation; * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001 (student’s t-test). ELK3, ETS transcription factor ELK3; Vector, control vector.