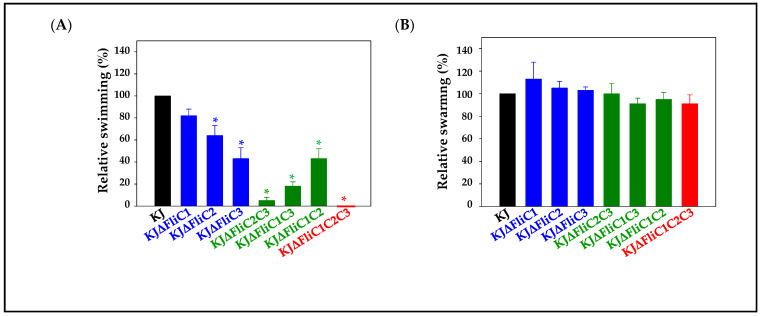
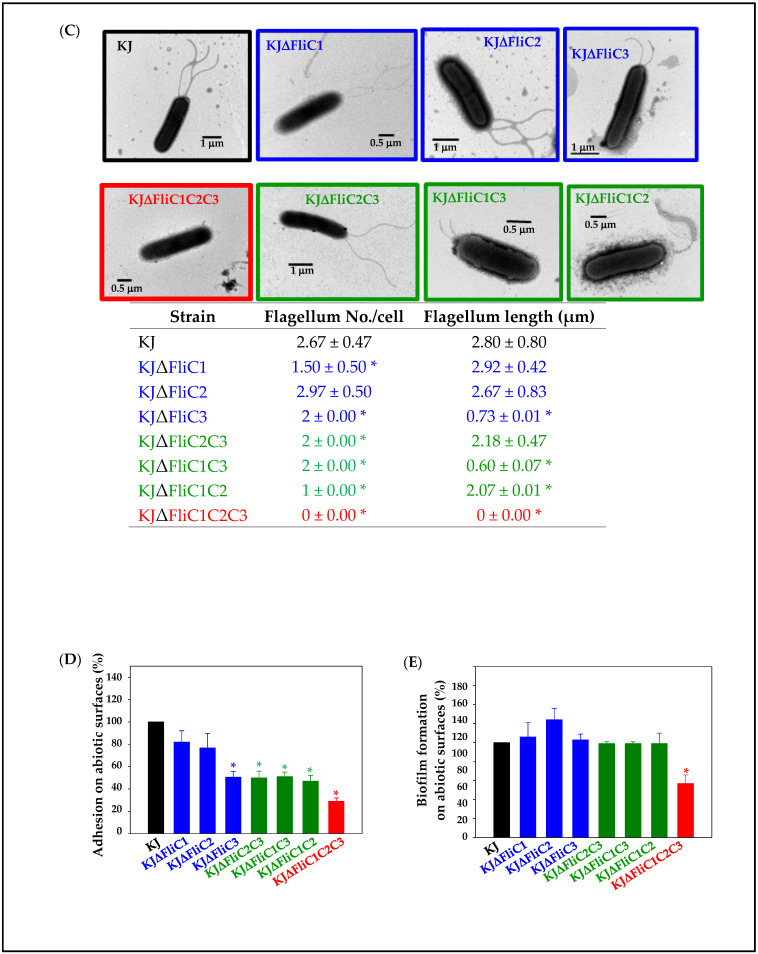
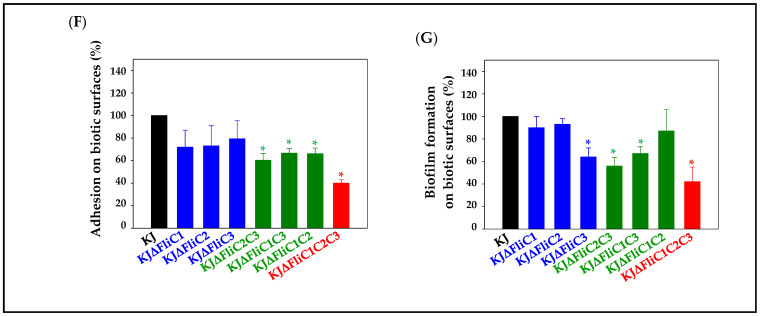
Figure 3.
The swimming, swarming, flagellum morphology, adhesion, and biofilm formation of wild-type KJ and its derived fliC-associated mutants. The color coding for black, blue, green, and red represent wild-type, single-deletion mutants, double-deletion mutants, and triple-deletion mutant. Data are the means from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviations for three triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05, significance calculated by Student’s t-test. (A) Swimming motility. Five microliters of overnight-cultured bacterial cell suspension was inoculated into swimming agar and then incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. The swimming zones were recorded. (B) Swarming motility. Five microliters of overnight-cultured bacterial cell suspension was inoculated into swarming agar and then incubated at 30 °C for 5 days. The swarming zones were recorded. (C) Flagella morphology. Overnight-cultured bacterial cells were inoculated into fresh LB broth and then grown for 5 h. The flagella were negatively stained with 1% phosphotungstic acid (pH 7.4) and observed by TEM. The average flagellum numbers per cell (at least 10 cells in each condition) and flagellum length (at least 20 flagella in each condition) were calculated. (D) Adhesion ability on abiotic surfaces. Tested S. maltophilia strain was adjusted to the concentration of 5 × 108 CFU/mL. Bacterial aliquot of 1 mL was inoculated into 24-well flat-bottom microplate and incubated at 37 °C for 2 h. The non-adherent bacteria were removed by PBS wash, and the adherent bacteria were quantified by CFU determination. (E) Biofilm formation on abiotic surfaces. Biofilm formation capacity of each strain was tested by the ability of the cells to adhere to the 96-well microplates, followed by crystal violet staining. (F,G) Adhesion ability and biofilm formation on biotic surfaces. The 293T cells were infected with analyzed S. maltophilia strain to obtain a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1000. After a 2-h (for adhesion ability) and 24-h (for biofilm formation) incubation, respectively, the non-adherent bacteria were removed by PBS wash, and the adherent bacteria were quantified by CFU determination.