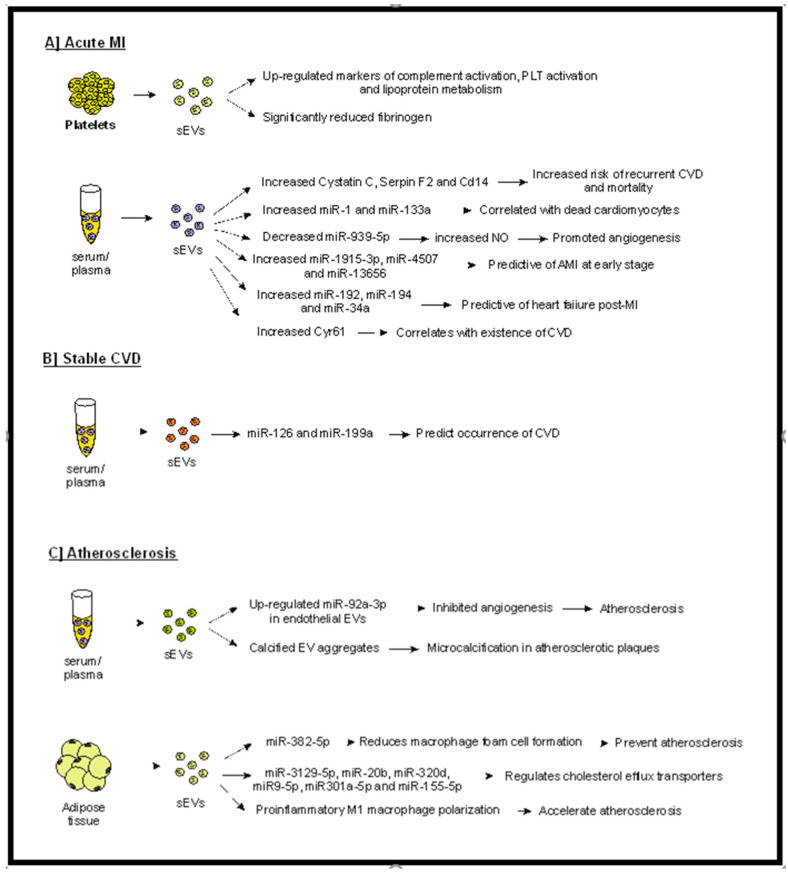
Figure 2.
Possible predictive role of sEVs in acute MI (A) in stable CVD (B) and in the generation of atherosclerotic plaques. (A) sEVs isolated from serum or plasma of patients with acute MI have been shown to carry various markers, such as miRNAs, cystatin C, serpin F2, CD14, and Cyr-6, that correlate with increased morbidity (e.g., heart failure, dead cardiomyocytes, CVD). Furthermore, factors associated with bad outcomes (such as complement activation and lipoprotein metabolism) have been detected in platelet-derived sEVs in patients with acute MI. (B) In patients with stable CVD, certain sEV-miRNAs can predict the progression of disease. (C) sEVs have been proven to participate in generation of atherosclerotic plaques, whereas adipose-derived sEVs have been shown to contribute to atherosclerosis development and progression. Abbreviations: sEVs: small extracellular vesicles, PLT: platelets, AMI: acute myocardial ischemia, CVD: cardiovascular disease, Cyr-61: cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61.