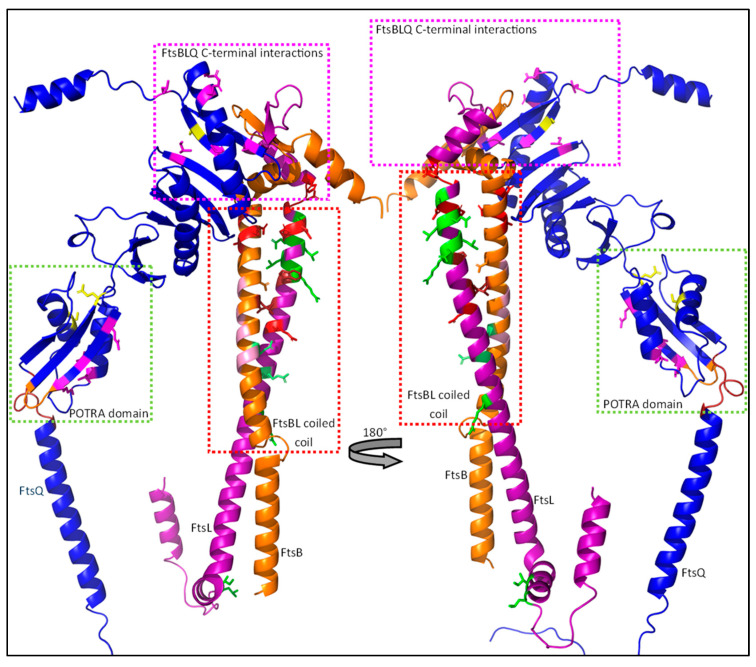
Figure 10.
The FtsBLQ regulatory subcomplex. Shown is the FtsBLQ subcomplex responsible for the regulation of the septal peptidoglycan synthesis machinery. The largest subunit, FtsQ, acts as a scaffold and comprises a small cytosolic domain, a transmembrane domain, and a large periplasmic domain. FtsB and FtsL have a similar structure, mostly consisting of a long helical structure, and form a coiled coil together. FtsB has a short cytoplasmic tail, while FtsL carries a large cytosolic double helical structure involved in the recruitment of FtsW. Regions or interactions that are important for sPG synthesis regulation are highlighted by the colored boxes and are further detailed in Figure 11 (POTRA domain), Figure 13 (FtsBL coiled coil) and Figure 15 (FtsBLQ C-terminal interactions). The structures shown here are predictions produced with AlphaFold2, advanced and visualized with the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.5.2 Schrödinger, LLC. Sequences for the prediction were obtained from the UniProtKB database (P06136-1 for FtsQ, Q9HXZ6-1 for FtsB and P0AEN4- for FtsL).