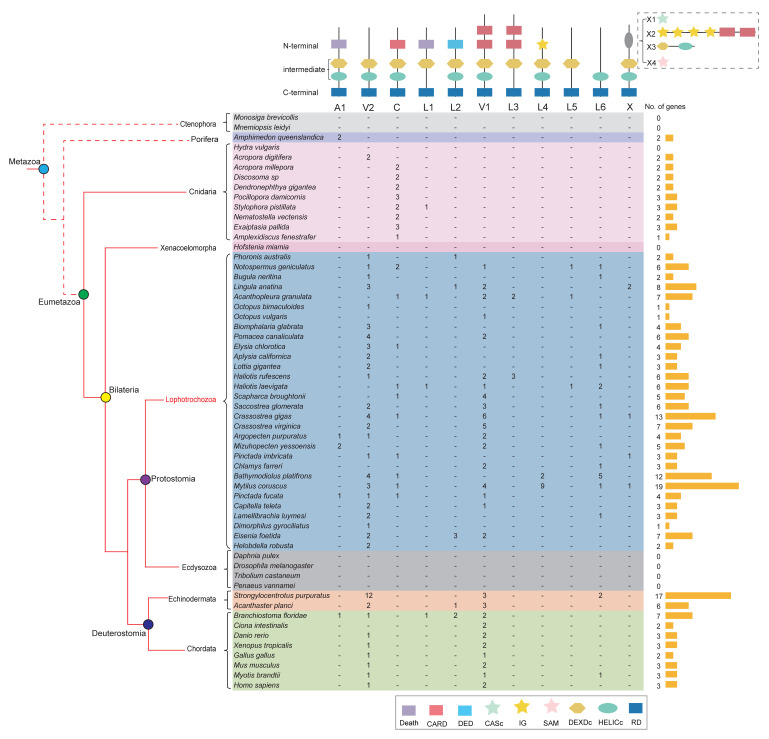
Figure 1.
Comparison of gene families encoding RLR immune receptors in representative animals across metazoans. Domain architecture in the lophotrochozoans is more complex than that in other clades. Species colors represent different phyla. Short lines indicate none of the RLRs in the subtype were annotated in this species. Phylogenetic relations among species are indicated by the red cladogram on the left of the table, and dashed lines represent unresolved phylogenetic positions for ctenophores and sponges. The column on the right counts the total number of RLR genes in each species and draws a yellow column chart. RLR diagrams show death family domain in purple, CARD domain in red, DED domain in light blue, CASc domain in light green, IG domain in light yellow, SAM domain in pink, DEXDc domain in yellow, HELICc domain in green, and RD domain in blue. Specifically, the top diagrams show A1, Amphimedon-like type 1; V1, vertebrate-like type 1; V2, vertebrate-like type 2; C, cnidaria-like type; L1, lophotrochozoa-like type 1; L2, lophotrochozoan-like type 2; L3, lophotrochozoan-like type 3; L4, lophotrochozoan-like type 4; L5, lophotrochozoan-like type 5; and L6, lophotrochozoan-like type 6. X implies four specific structural features (X1–X4).