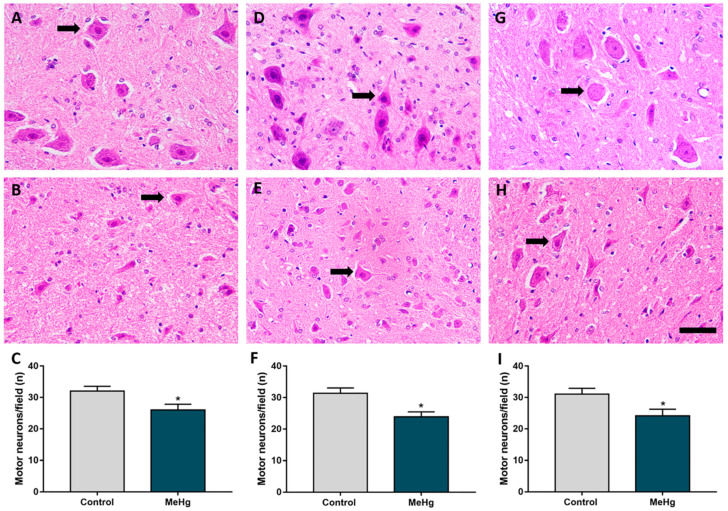
Figure 2.
MeHg caused a reduction in the density of motoneurons in all areas evaluated. Effect of MeHg on the cervical (A–C), thoracic (D–F) and lumbar (G–I) segments of the spinal cord in the offspring rats (n = 7 animals per group) after exposure during the intrauterine and lactation periods to 40 μg/kg/day of MeHg (samples collected 21 days after 42 days of dosing). (A,D,G) are representative photomicrographs of the motoneuron counts in the control group and (B,E,H) in the exposed group. In (C,F,I) are the results of the motoneuron density, expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 7–8 animals per group). * p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. Black arrows indicate motoneurons. Scale bar: 20 μm.