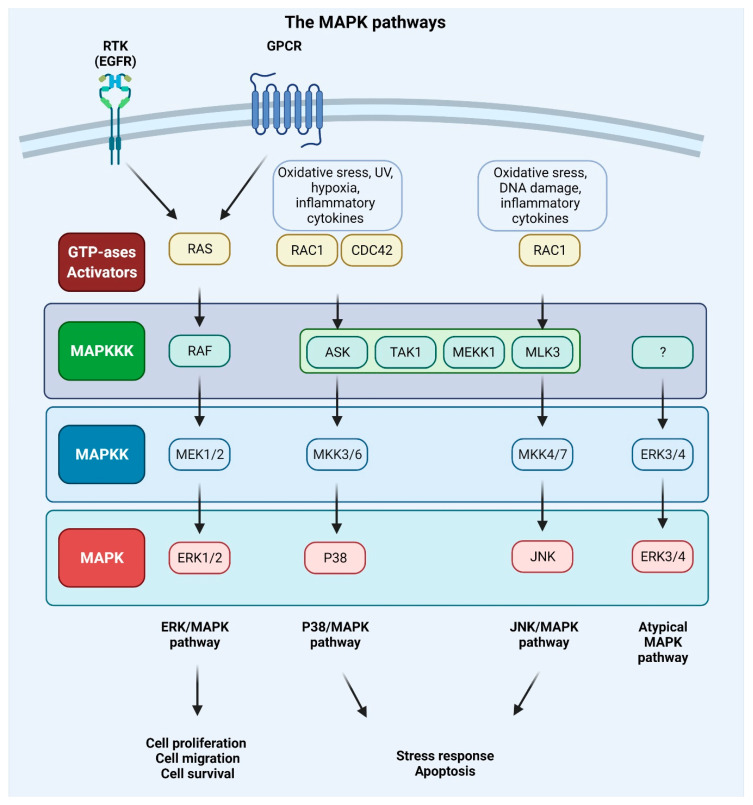
Figure 4.
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Extracellular signals such as growth factors and cytokines, as well as intracellular signals such as oxidative and DNA damage, activate MAPK pathways. GTPases (activators) such as RAS, RAS-related protein (RAC), and cell division control protein 42 homolog (CDC42) constitute the first layer of MAPK signaling cascade, which conveys the signal to downstream protein kinases. The MAPK signaling cascades consist of three kinases: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK), a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and results in proliferation, migration, differentiation, survival, or apoptosis. Mammalian MAPK pathways include ERK MAPK, P38 MAPK, and JNK MAPK signaling events. ERK/MAPK pathway is activated by RAS, which is attracted to the plasma membrane through receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and G protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) activation. In this cascade, MAPK/ERK kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). P38/MAPK and JNK/MAPK pathways are triggered by various insults that activate signaling through MKK3/6 or MKK4/7 (MAPKKs), respectively, that are activated upon MAPKKK s such apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1), transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), MEKK1 (MAPKKK), and MLK3 (MAPKKK). ERK3/4 are considered atypical MAPK kinases [156].