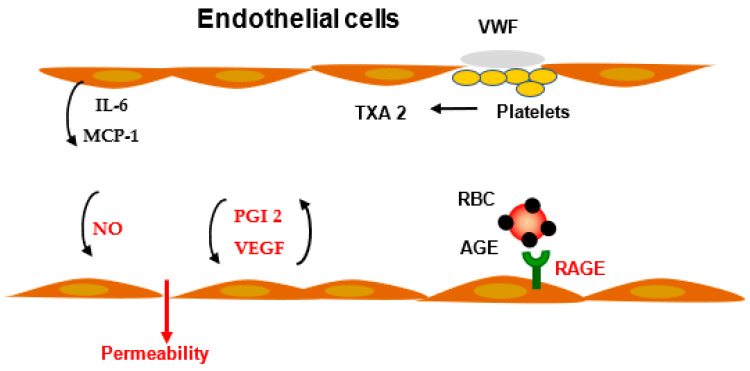
Figure 3.
Modulation of vascular permeability and inflammation. Activated EC produced and released interleukin-6 (IL-6) and macrophage (monocyte) protein-1 (MCP-1) in inflammatory conditions. Advanced glycation end products (AGE), present on protein or red blood cell (RBC), bind to a specific receptor (RAGE), inducing a cascade of reactions, resulting in an increased vascular permeability. Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the mediators for vascular tone and vascular permeability. Prostacyclin (PGI 2) modulates vascular pressure and permeability. Activated platelets, after adhesion to the matrix and von Willebrand factor (VWF), release thromboxane A2 (TXA2), which contributes to permeability regulation.