Figure 10.
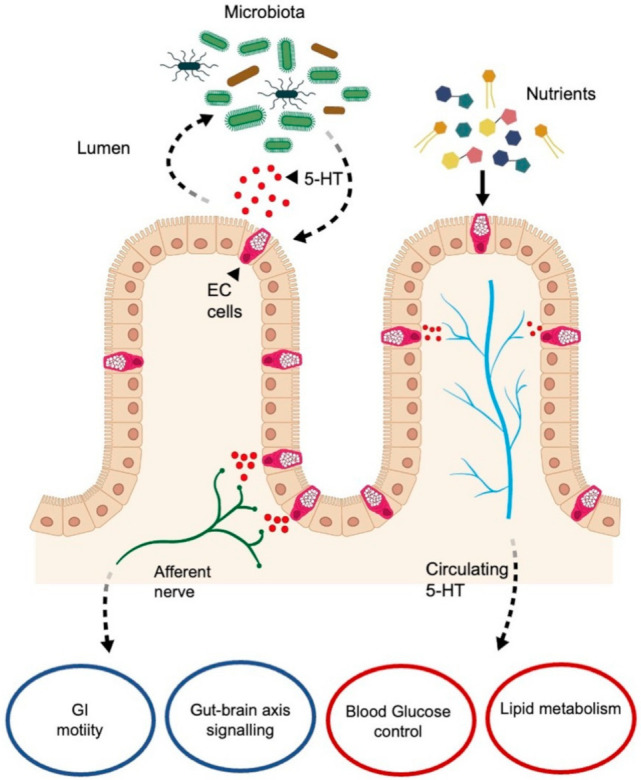
Schematic representation of the bidirectional relationship among ECs, enteric nervous system, 5-HT, nutrients, and microbiota. 5-HT released from EC cells can modulate the microbiota species, but moreover, once released in the blood stream, it could stimulate glucose and lipid metabolism. Basal 5-HT’s release can also activate vagal afferent fibers inducing intestinal motility and modulating the brain–gut axis signaling. EC cell: enterochromaffin cell; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine; GI: gastrointestinal. Black arrows and black dotted arrows represent the relationship between intestinal mucosa, the nervous system, the circulatory system and the lumen’s content. Modified from Jones et al., 2020 [12].
