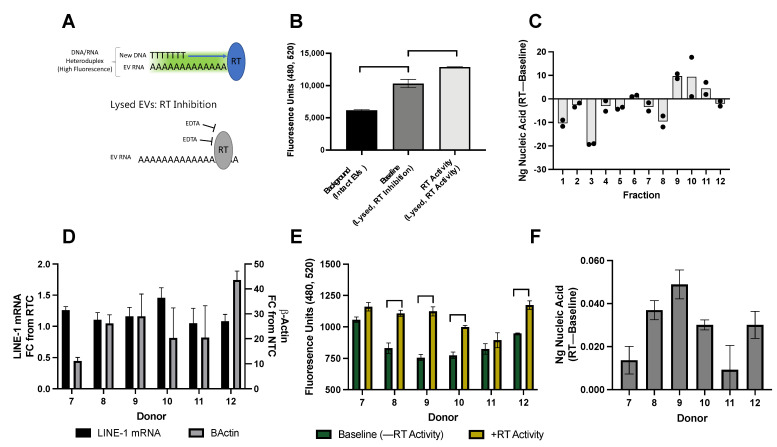
Figure 6.
Reverse transcriptase activity in EVs from BaP stimulated cells and healthy plasma donors. (A) The modified ENZ-check reverse transcriptase (RT) activity assay indicates the presence of EV-derived reverse transcriptase (RT) and its ability to use extracellular vesicle (EV) mRNA and DNA as a template. During the reaction, any reverse transcriptase enzyme (i.e., ORF2p) will use EV mRNA and DNA to form RNA-DNA heteroduplexes, which bind PicoGreen and emit a fluorescent signal. This RT signal is normalized to baseline fluorescence emitted by EV DNA cargo, which is measured by inhibiting RT activity with EDTA. EVs were collected by ultracentrifugation. (B) Determination of baseline fluorescence and RT activity. Raw fluorescence of RT activity, background, and baseline conditions. “Background, Intact EVs” reaction constituents and PicoGreen are prevented from accessing EV cargo as the EV lipid membrane is still intact. “Baseline, RT Inhibition” EVs are lysed allowing PicoGreen to bind with DNA cargo but EDTA prevents RT activity. “RT Activity” EVs were lysed and conditions permissive for RT activity. One-way ANOVA: p < 0.05. (C) RT activity in EVs collected from BaP-treated cells. Fractions from Figure 2 were examined for RT activity and a DNA standard curve was used to quantify the amount of new nucleic acid generated in the RT reaction. To detect RT activity in individual plasma donors, EVs were isolated from 2.5 mL plasma via ultracentrifugation. Half the preparation was used for mRNA quantification and the other for RT activity measurement. The age and sex of plasma donors are shown in Figure 5D. (D) EV Long Interspersed Element-1 (LINE-1) mRNA and β-Actin levels. (E) Nucleic acid fluorescence. RT activity assay showing raw fluorescence values of baseline and RT activity conditions. p < 0.05: two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons. (F) EV RT activity measurement in ng of nucleic acid. Mean, SD shown.