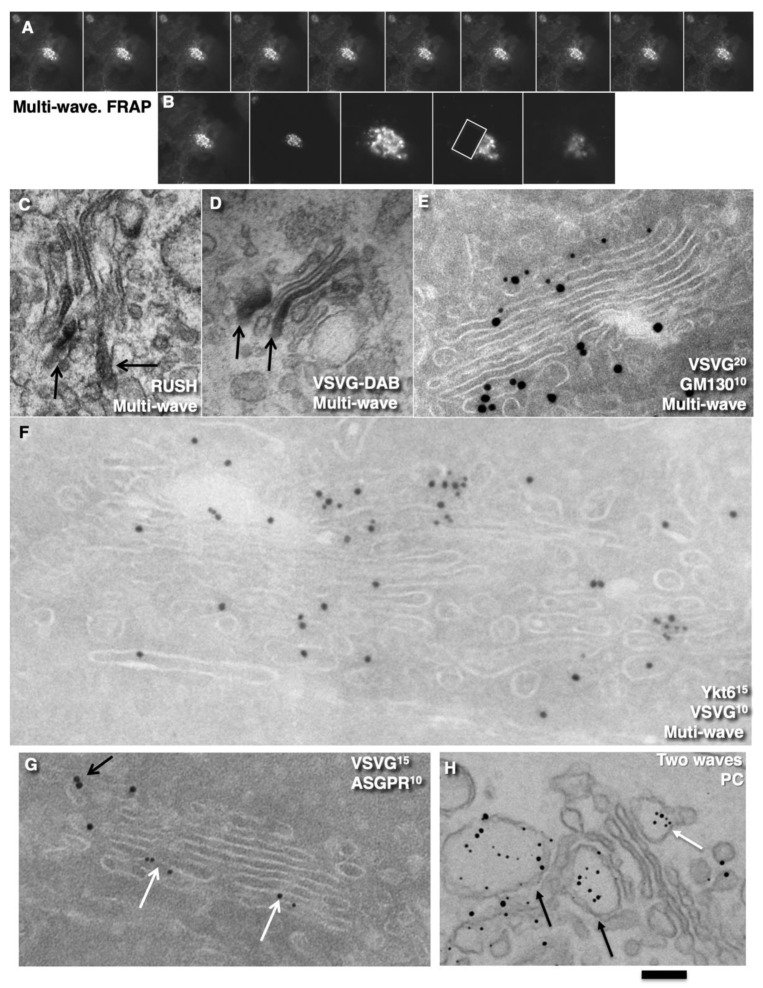
Figure 8.
Multi-wave synchronization protocol. HeLa (A-F), HepG2 (G) cells, and human fibroblasts (H) were subjected to multi-wave synchronisation protocols (see Methods). (A,B) Fluorescent microscopy. (A) Kymographs of VSVG-GFP dynamics within the Golgi mass. Carriers moved in both directions. (B) Kymographs of the same Golgi mass (two first images), higher magnification (middle image), and subsequent bleaching of half of the Golgi complex. (C) Immuno-peroxidase labelling for RUSH-TNF-α in different Golgi cisternae (arrows) after synchronisation according to multi-wave intra-Golgi transport (see Methods). (D) After the multi-wave protocol, VSVG is present in different cisternae (immuno-peroxidase labelling; DAB). (E) Tokuyasu cryo-sections. VSVG is present in the first near Golgi cisterna (GM130) and the last medial Golgi cisternae. (F) Tokuyasu cryo-sections. Distinct domains of VSVG (10-nm gold) contain enriched Ykt6 (15-nm gold). (G) Tokuyasu cryo-sections. In HepG2 cells infected with tsVSV and synchronised according to the CHM-15-CHM protocol, VSVG and ASGPR form distinct domains at 5 min after release of the transport block. (H) In human fibroblasts, after arrival of the second wave of PC, the first portion (white arrow) was already at the trans-side (black arrows) of the stack. Enhanced nano-gold. Scale bars: 8 µm (A); 6 µm (B); 210 nm (E); 250 nm (C,H); 85 nm (F); 170 nm (G).