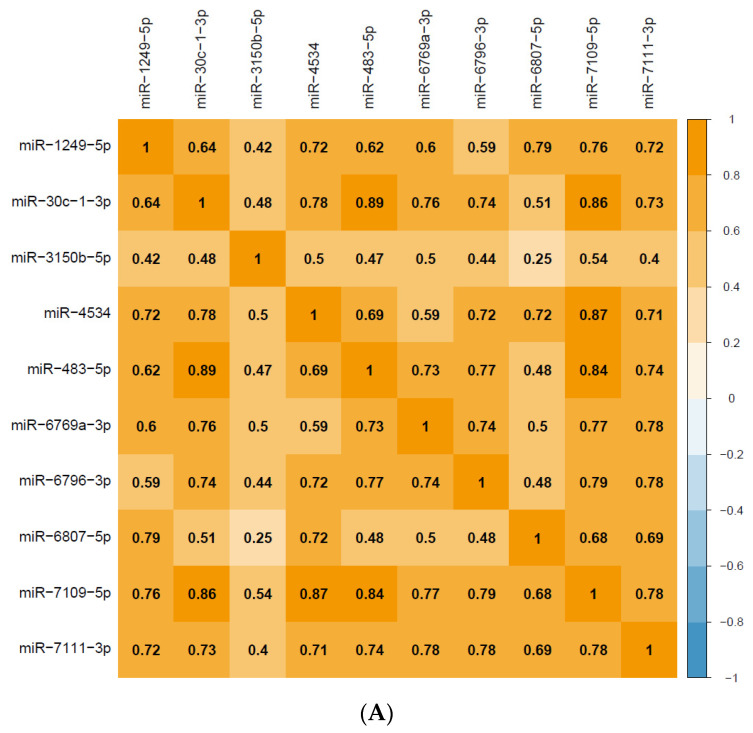
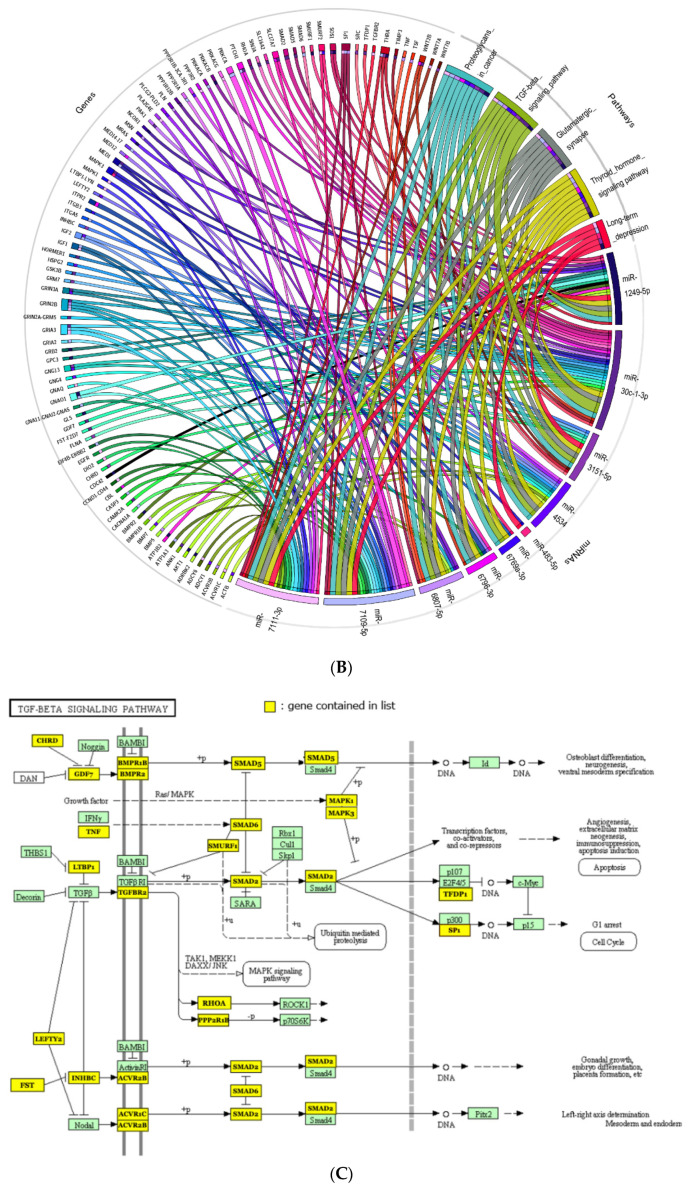
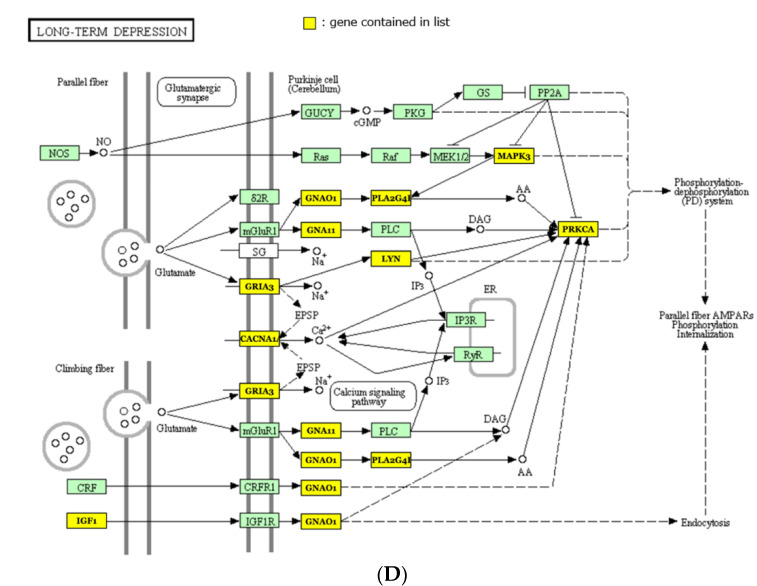
Figure 2.
(A) A correlation matrix between pre-treatment miRNAs in major depressive disorder patients that were strongly associated with Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score reductions after 2 weeks of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment. Caption: The numbers indicate the correlation coefficients. (B) Circos plot of the top 10 miRNAs associated with HAM-D score reduction after 2 weeks of SSRI treatment and the interacting genes and pathways. Caption: After conservative stats based on the probability of jackknifing tests and FDR correction, of 21 pathways that were significantly associated with these 10 miRNAs(miR-483-5p, miR-3151-5p, miR-7109-5p, miR-6807-5p, miR-30c-1-3p, miR-6769a-3p, miR-7111-3p, miR-6796-3p, miR-1249-5p, miR-4534), the five pathways (TGF-β signaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer, Long-term depression, Glutamatergic synapse, and Thyroid hormone signaling pathway) and 95 genes that showed the strongest association (adjusted p < 0.01) are shown. Each ribbon connects an miRNA with predicted target genes and pathways. The width of the ribbon is proportional to the number of results indicating the interaction. (C) Modified “TGF-beta signaling pathway” from KEGG. Caption: The genes in the yellow squares are statistically robust interactions with the top 10 miRNAs associated with HAM-D score reduction after 2 weeks of SSRI treatment. (D) Modified “Long-term depression” from KEGG. Caption: The genes in the yellow squares are statistically robust interactions with the top 10 miRNAs associated with HAM-D score reduction after 2 weeks of SSRI treatment.