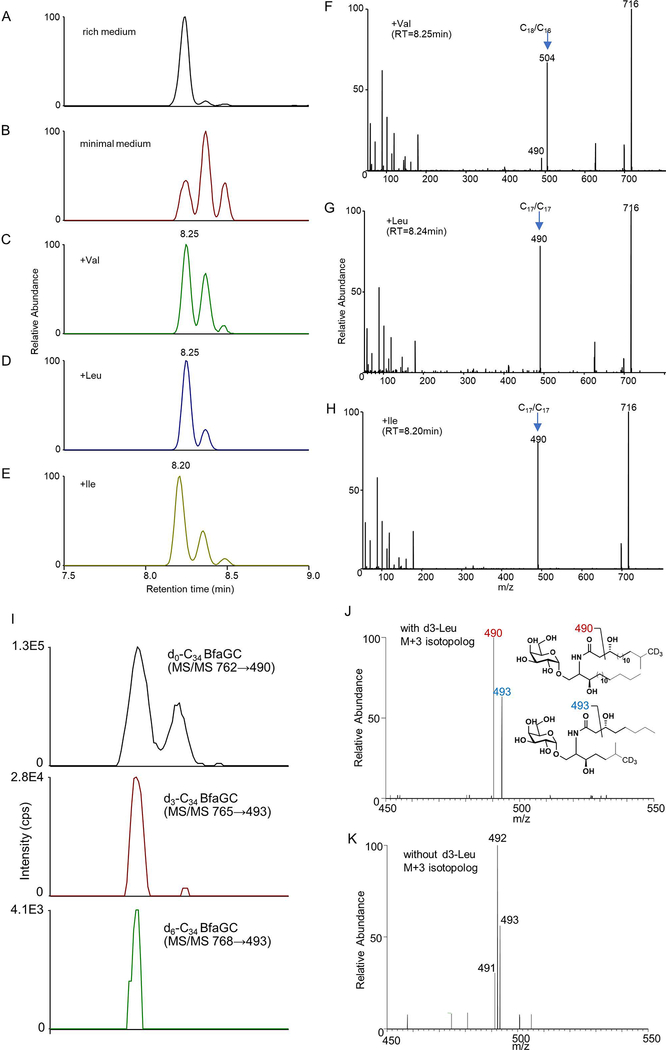
Extended Figure 5. BCAA dictates branching of BfaGCs by direct incorporation in vivo.
(A–E) Ratios among differently branched C34 BfaGCs (MS1 XIC=762.57, as [M+HCOO-]) are clearly different for B. fragilis grown in rich medium (A) and B. fragilis grown in minimal medium (B). Supplementation with individual BCAAs (C–E) on defined medium increases production of branched-chain (both dibranched and monobranched) BfaGCs. (F–H) MS/MS fingerprints confirm the incorporation of leucine and isoleucine into the C17/C17 ceramide backbone (via C5 branched acyl-CoA) and of valine into the C18/C16 backbone (via C4 branched acyl-CoA). Chromatograms and spectra are representative of triplicate observations. (I) An MS/MS-XIC of d3- and d6-C34 BfaGC shows that deuterium-labeled leucine is actively incorporated into BfaGC. (J-K) MS/MS pattern shows distinctive differences between gut luminal BfaGC (M+3 isotopolog) in (J) presence or (K) absence of d3-leucine, showing MS2 fragments in presence of d3-leucine reflect inclusion of deuterium-labeled leucine in the structure. Chromatograms and spectra are representative results of four mice.