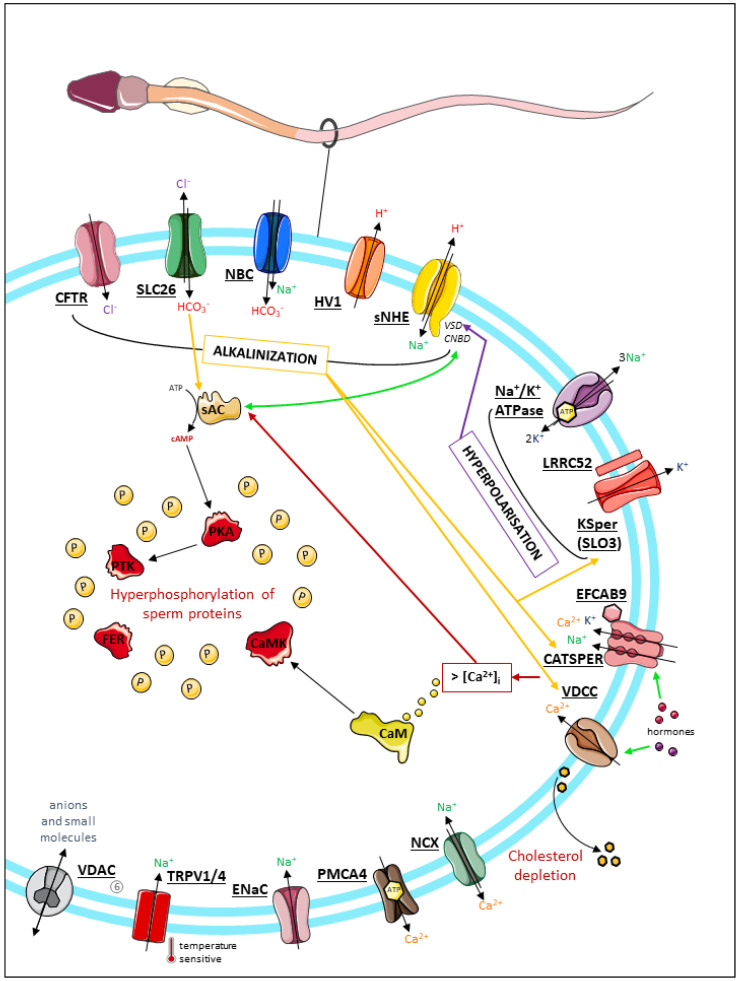
Figure 1.
Scheme summarizing the main molecular, biochemical, and electrophysiological events associated with sperm capacitation and the main ion channels/transporters involved in the process. The first subset of ion channels (SLC26 family interacting with CFTR, NBC, Hv1, and sNHE) are responsible for intracellular alkalinization of the sperm by internalizing bicarbonate or extruding protons. The subsequent pH increase is responsible for sAC activation, which induces an increase in intracellular cAMP. cAMP is a key element of sperm signaling during capacitation, in particular, by mediating PKA-dependent phosphorylation events and also by promoting the activity of other ion channels, such as CatSper, VDCC, and KSper (yellow arrows). CatSper and VDCC mediate Ca2+ entry into spermatozoa and are sensitive to the stimulation of progesterone and other hormones present in the female genital tract. The increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration also participates in the activation of sAC (red arrow). In addition, membrane hyperpolarization by cation extrusion through KSper and Na+/K+ ATPase also influences voltage-sensitive actors, such as sNHE (violet arrow). It also temporally regulates the activity of other channels, as it inhibits CatSper and Hv1 (Vyklicka and Lishko, 2020). Of note, Hv1 is absent from murine spermatozoa; this voltage-gated channel is specific to human sperm cells, in which it is restricted to the principal piece of the flagellum within two bilateral longitudinal lines asymmetrically interacting with the four CatSper nanodomains [26]. CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; SLC26, solute carriers family 26; NBC, Na+/HCO3− cotransporter; Hv1, voltage-gated H+ channel; sNHE, sperm-specific Na+/H+ exchanger; LRRC52, leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 52; KSper, K+ sperm channel; EFCAB9, EF-hand Ca2+-binding domain-containing protein 9; CatSper, cation sperm channel; VDCC, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel; NCX, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger; PMCA4, plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase4; ENaC, epithelial Na+ channel; TRPV4, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel. This picture contains graphical elements obtained from smart.servier.com (accessed on 20 March 2022).