Table 1.
Characteristics of the most stable bimolecular hetero-molecular complexes formed by caffeine in analyzed solutions. Primes in the geometry parameters denote atoms of solvent molecules. The values of Gibbs free energy of reaction represent the concentration-independent quantity derived using activities at 25 °C.
| caffeine–DMF | caffeine–DMSO | ||
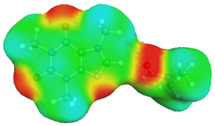 dH⋯O’ = 2.149 Å, αC-H⋯O’ = 176.3° ΔGr(AB) = −5.7 kcal/mol |
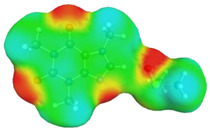 dH⋯O’= 2.105 Å, αC-H⋯O’= 179.1° ΔGr(AB) = −6.5 kcal/mol |

|
+0.01e2/Å2 −0.01e2/Å2 |
| caffeine–1,4-dioxane | caffeine–acetone | ||
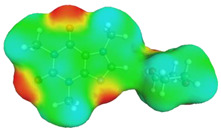 dH⋯O’ = 2.192 Å, αC-H⋯O’ = 176.5° ΔGr(AB) = −5.0 kcal/mol |
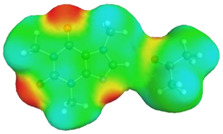 dH⋯O’ = 2.283 Å, αC-H⋯O’ = 175.5° ΔGr(AB) = −4.2 kcal/mol |
||
| caffeine–acetonitrile | caffeine–water | ||
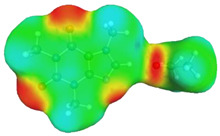 dH⋯O’ = 2.388 Å, αC-H⋯O’ = 175.5° ΔGr(AB) = −3.5 kcal/mol |
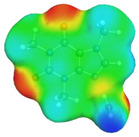 dN⋯H’ = 1.852 Å, αC-H⋯O’ = 177.3° ΔGr(AB) = −6.4 kcal/mol |
||
