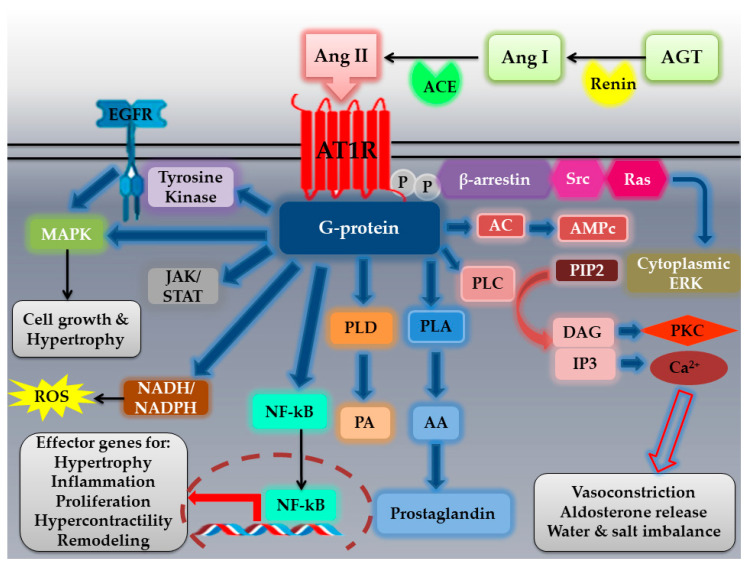
Figure 2.
Angiotensin II type I receptor (AT1R) activation by angiotensin II (Ang II) and its signaling pathways. Ang II is produced from the conversion of AGT to Ang I by renin, and then, Ang I is cleaved by ACE into Ang II. Ang II is recognized by a G-protein-coupled receptor, AT1R. The agonist ligand (Ang II) binding to AT1R activates several signal transduction pathways, including noncanonical downstream effectors such as PLA, PLD, and PLC generating AA, PA, and IP3 and DAG, respectively. In turn, IP3 and DAG lead to Ca2+ and PKC activation, respectively implicated in water and salt balance, as well as aldosterone release and vasoconstriction. Canonical GPCR signaling activates receptor tyrosine kinases such as EGFR, as well as activating the NADPH complex, resulting in the generation of ROS, a potent second messenger implicated in oxidative stress. In addition, AT1R stimulation results in activation of MAPK and NF-κB transactivation. Together, this leads to pathophysiological responses such as hypertrophy, hypercontractility, proliferation, matrix production, inflammation, vascular remodeling, and hypertension. JAK/STAT activation by AT1R is involved in promoting cellular survival, migration, adhesion, and apoptosis. Moreover, AT1R rapidly undergoes desensitization through phosphorylation, which leads to β-arrestin recruitment, binding, and activation of MAPK-dependent signaling cascade. In fact, β-arrestin serves as a scaffold for signaling effectors such as Src, resulting in downstream activation of cytoplasmic ERK. AGT: angiotensinogen; Ang I: angiotensin I; ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; Ang II: angiotensin II; AT1R: angiotensin II type 1 receptor; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; JAK/STAT: Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription; NADH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ROS: reactive oxygen species; NF-κB: nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PLD: phospholipase D; PLA: phospholipase A; PLC: phospholipase C; PA: phosphatidic Acid; AA: arachidonic acid; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate; DAG: diacylglycerol; IP3: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; PKC: protein kinase C, Ca2+: calcium; AC: adenylate cyclase; AMPc: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase.