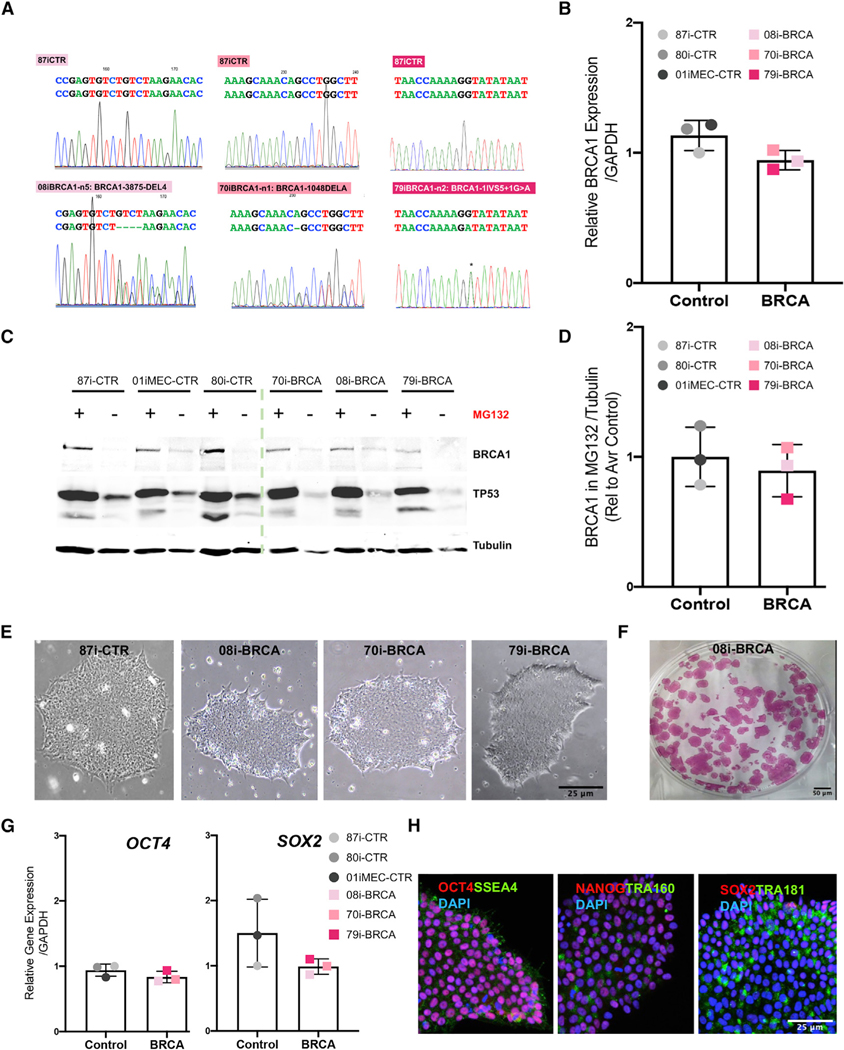
Figure 1. Characterization of BRCA1mut and control iPSC lines.
Lines 87i-CTR-n3, 80i-CTR-Tn3, 01iMEC-CTR-n4, 08i-BRCA-n5 and -n8, 70i-BRCA-n1 and -n2, and 79i-BRCA-n2 were characterized.
(A) Sequence analysis of heterozygous BRCA1mut in iPSC lines 79i-BRCA (IVGS5+1G > A located at the junction between exon 5 and intron 6), 70i-BRCA (1048delA), and 08i-BRCA (3875del4 located in exon 11). Heterozygous positions are indicated in comparison to 87i-CTR.
(B) BRCA1 gene expression in all controls and BRCA1mut-iPSC lines.
(C) Western blot for BRCA1, TP53, and Tubulin protein in iPSC lines after a 24-h treatment with the MG132 proteasomal inhibitor.
(D) BRCA1 protein normalized to Tubulin and quantified from multiple iPSC lines, with each point representing the band intensity from a separate line.
(E) Brightfield image of iPSC colonies for 87i-CTR, 08iBRCA, 70iBRCA, and 79iBRCA.
(F) Representative image of alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining of the 08i-BRCA line.
(G) Relative gene expression of OCT4 and SOX2 genes in all iPSC lines. Relative gene expression to 87i-CTR calculated using DDCt method and normalized to the endogenous GAPDH level.
(H) Immunocytochemistry of the 79i-BRCA iPSC line for pluripotent stem cell markers OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, TRA160, TRA181, and SSEA4. Scale bars, 25 μm. Error bars are standard error of the mean (SEM) (n = 3 independent biological experiments and each dot represents the average of 3 independent biological experiments per line).