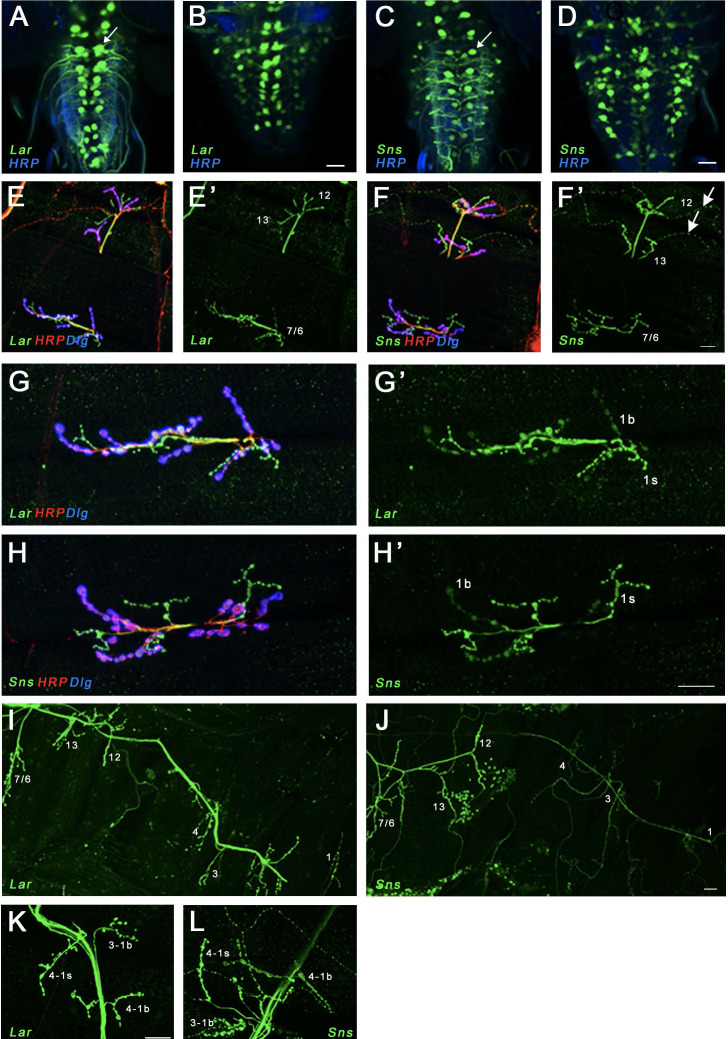
Figure 2. Expression of Lar and Sns reporters in motor neurons.
(A–D) Confocal projections of 4–6 optical slices showing EGFP expression driven by either LarMI02154-T2A-GAL4 (Lar>GFP) or SnsMI03001-T2A-GAL4 (Sns>GFP) (green) co-stained with anti-HRP (blue). The bright paired midline cells include motor neurons (A, C, arrows). (E–H’) Confocal projections of larval neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) on muscles 7/6, 13, and 12 (E, F’) and zoomed-in on muscle 7/6 (G, H’), triple-stained with anti-GFP (green), anti-HRP (red), and anti-Dlg (blue). (E’, F’, G’, H’) show GFP signal only. Anti-HRP labels neuronal membranes, and anti-Dlg labels the subsynaptic reticulum at 1b boutons. Lar>GFP and Sns>GFP expression is seen in both 1b and 1s boutons (green), while only Sns>GFP is seen in type II boutons (F’, arrows). (I, J) Projection of optical slices through an entire larval hemisegment showing Lar>GFP (I) and Sns>GFP (J) expression in both 1b and 1s motor neurons. Individual muscles are numbered. Dorsal is to the right. Note that Lar>GFP is equally expressed in most axons and NMJs, while Sns>GFP is expressed at lower levels in axons and NMJs of motor neurons projecting to dorsal muscles. (K, L) Close-up of NMJs on muscles 3 and 4 showing both Lar>GFP (K) and Sns>GFP (L) expression in 1b and 1s NMJs on those muscles. Scale bar, 20 µm. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for further characterization of Lar and Sns expression in the larval ventral nerve cord (VNC) and central nervous system (CNS).