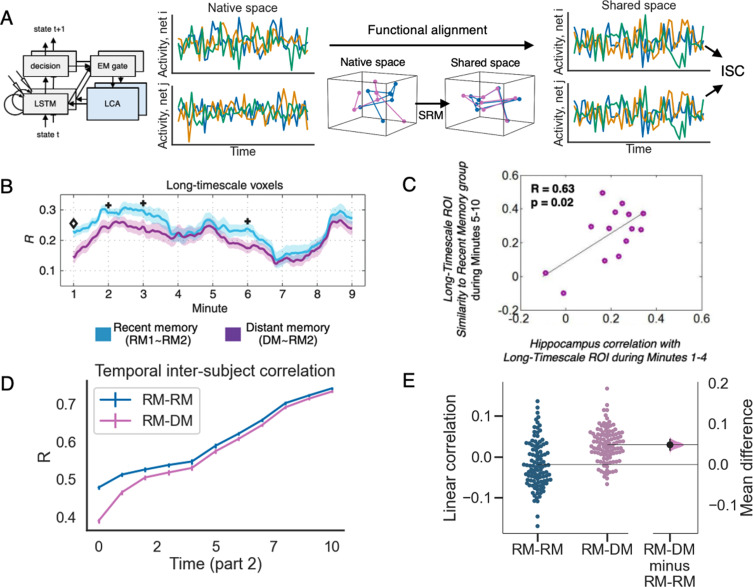
Appendix 6—figure 1. Simulating inter-subject correlation results from Chen et al., 2016.
(A) Illustration of how we computed inter-subject correlation (ISC) in the model (see text for details). (B and C) show the empirical results from Chen et al., 2016 (reprinted with permission) and (D and E) show model results. (B) The sliding-window temporal inter-subject correlation (ISC) over time, during part 2 of the movie. The recent memory ISC, or RM-RM ISC, was computed as the average ISC value between two non-overlapping subgroups of the RM participants. The distant memory ISC, or RM-DM ISC, was computed as the average ISC between one sub-group of RM participants and the DM participants. Initially, the RM-DM ISC was lower than RM-RM ISC, but as the movie unfolded, RM-DM ISC rose to the level of RM-RM ISC. (C) For the DM participants, the level of hippocampal-neocortical inter-subject functional connectivity at the beginning of part 2 of the movie (minutes 1–4) was correlated with the level of RM-DM ISC later on (minutes 5–10). (D) Sliding window temporal ISC in part 2 between the RM models (RM-RM) compared to ISC between the RM and DM models (RM-DM). The convergence between RM-DM ISC and RM-RM ISC shows that activity dynamics in the DM and the RM models become more similar over time (compare to part B of this figure). The errorbars indicate 1SE across 15 models. (E) The correlation in the model between memory activation at time and the change in ISC from time to time , for the first 10 time points in part 2. Each point is a subject-subject pair across the two conditions. The 95% bootstrap distribution on the side shows that the correlation between memory activation and the change in RM-DM ISC is significantly larger than the correlation between memory activation and the change in RM-RM ISC (see text for details).
© 2016, Oxford University Press Permissions
panel B is reprinted from Figure 6 Chen et al., 2016 by permission of Oxford University Press. It is not covered by the CC-BY 4.0 licence and further reproduction of this panel would need permission from the copyright holder
© 2016, Oxford University Press Permissions
panel C is reprinted from Figure S7 Chen et al., 2016, by permission of Oxford University Press. It is not covered by the CC-BY 4.0 licence and further reproduction of this panel would need permission from the copyright holder