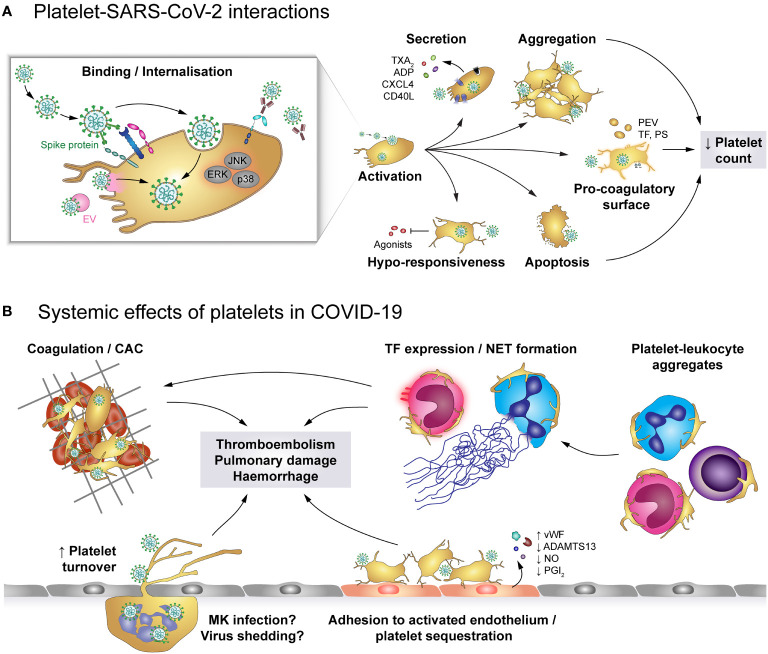
Figure 6.
The role of platelets in COVID-19. (A) SARS-CoV-2 may enter platelets upon binding to ACE2/TMPRSS2 or EMMPRIN receptors or by hitchhiking on extracellular vesicles (EV) that fuse with the platelet plasma membrane, though SARS-CoV-2-containing immune complexes are also recognised by FcγRIIA. Binding and/or internalisation of SARS-CoV-2 stimulates platelet activation including degranulation and secretion, integrin activation and aggregation as well as exposure of pro-coagulant surfaces on platelets themselves or platelet-derived extracellular vesicles (PEV). Together with apoptosis of virus-bound platelets, these processes induce a reduction in circulating platelet count. Platelet hyper-activation in COVID-19 is accompanied by hypo-responsiveness to further stimulation. (B) Altered platelet behaviour in COVID-19 has systemic effects on pro-thrombotic and immunomodulatory platelet functions. Hyper-active and pro-coagulant platelets show enhanced adhesion to the inflamed endothelium and foster the development of COVID-19-associated coagulopathy (CAC). Accordingly, platelet turnover is increased in COVID-19. Formation of platelet-leukocyte aggregates triggers monocyte TF expression and NET formation, which add to the pro-coagulant microenvironment. In addition, infected megakaryocytes may shed virions to exacerbate infection. Together, these pathologic alterations increase the risk for thromboembolisms, pulmonary damage and haemorrhages. ACE2, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ADAMTS13, A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13; CAC, COVID-19-associated coagulopathy; CD40L, CD40 ligand; COVID-19, Coronavirus-induced disease 2019; CXCL4, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 4; EMMPRIN, extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer; ERK, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FcγRIIA, Immunoglobulin γ Fc region receptor IIA; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; MK, Megakaryocyte; EV, Extracellular vesicle; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; PEV, Platelet-derived extracellular vesicle; NO, Nitric oxide; PGI2, Prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin); PS, phosphatidylserine; SARS-CoV-2, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TF, Tissue factor; TMPRSS2, Transmembrane protease serine subtype 2; TXA2: thromboxane A2; vWF, von Willebrand factor.