Figure 2.
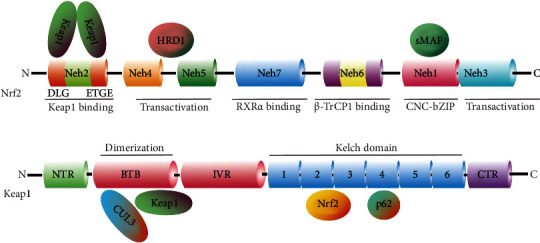
Structures of Nrf2 and Keap1 protein domains. (a) Nrf2 consists of 589 amino acids and has seven evolutionarily highly conserved domains (Neh1-7). Neh1 contains a bZIP motif and is responsible for DNA recognition and mediates the dimerization with the small MAF (sMAF) protein. Neh6 acts as a degron to mediate the degradation of Nrf2 in the nucleus. Neh4 and 5 are transactivation domains. Neh2 contains ETGE and DLG motifs which are required for the binding of Nrf2 to Keap1. Neh7 is a domain that interacts with RXRα to inhibit CNC-bZIP factors and the transcription of genes. Neh3 regulates CHD6. (b) Keap1 consists of 624 amino acids and has five domains. BTB domain together with the N-terminal region (NTR) of IVR to mediate the homodimerization of Keap1 and binding to Cul3. The Kelch domain and the C-terminal region (CTR) mediate the interaction with Neh2 of Nrf2 at the ETGE and DLG motifs.
