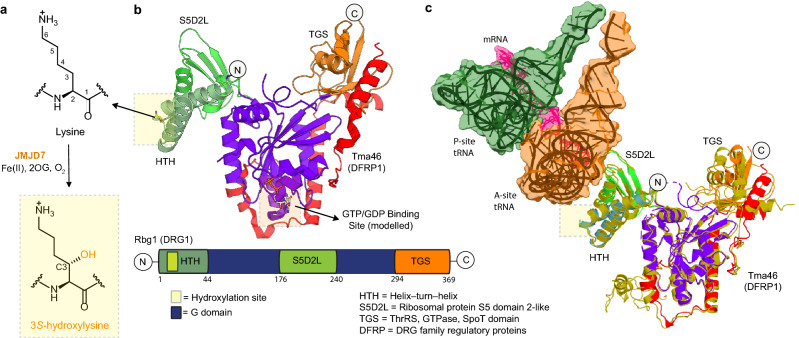
Figure 1.
Lysyl hydroxylation sites in DRG1 and 2. (A) JMJD7-catalysed (3S)-lysyl hydroxylation. (B) Views from a crystal structure of Rbg1.Tma46 complex (the yeast homologue of human DRG1.DFRP1, PDB: 4A9A) highlighting the hydroxylation site. All DRG orthologues, including Rbg1, contain three additional domains (HTH, S5D2L and TGS) surrounding the GTPase domain. JMJD7 hydroxylates a highly conserved lysine residue at the apex of the DRG HTH domain (boxed yellow; see Figs. S1b and S2a for an alignment of DRG orthologues). (C) Views from the cryo-EM structure of yeast 80S ribosome bound to Rbg1.Tma46 complex (PDB: 7RR5, EMD-24652) showing molecular interactions between Rbg1 and the ribosomal A-site tRNA (for simplicity, the rest of the ribosome is not shown)14. The figure shows superimposed views of the Rbg1.Tma46 complexes in the free (PDB: 4A9A, colour coded as in (B) and ribosome-bound (PDB: 7RR5, golden-yellow) forms revealing conformational changes, particularly involving the Rbg1-TGS domain and Tma46 on ribosome binding. Given that the target lysine sidechain is in close contact with A-site tRNA, hydroxylation may affect interactions with the ribosome.