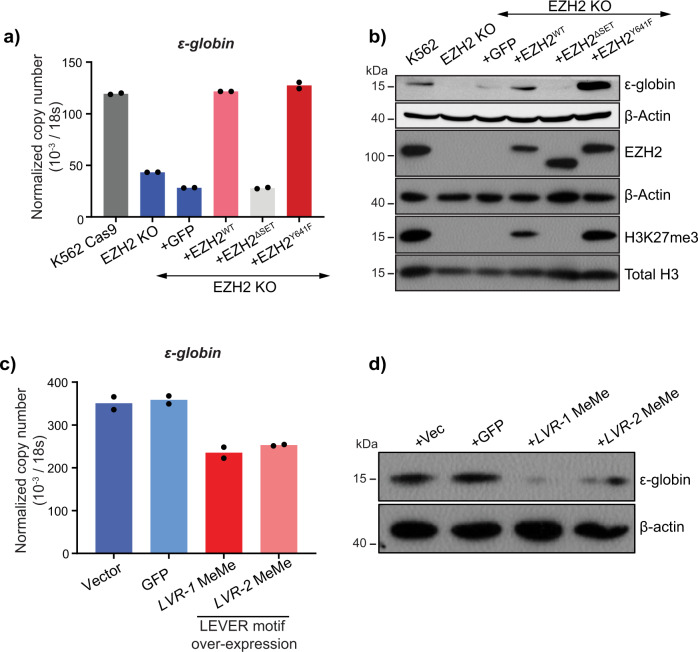
Fig. 3. PRC2 enzymatic function maintains ε-globin expression in K562.
a RT-qPCR analysis of ε-globin in K562 Cas9-expressing parental cells, EZH2 knock-out (EZH2-KO) cells, and EZH2-KO cells rescued with GFP, EZH2, EZH2ΔSET, and EZH2Y641F. EZH2ΔSET, truncated EZH2 without methyltransferase enzymatic domain; EZH2Y641F, EZH2 gain of methyltransferase enzymatic function mutation. The EZH2-KO cells were transduced with lentivirus to stably express these constructs. Data from technical replicates of one biological sample is shown. b Western blot analysis of ε-globin, EZH2, and global H3K27me3 in K562 wild type, EZH2 KO, and rescue cells as in a. β-actin and total histone H3 were used as loading controls. c, d ε-globin expression in LEVER KO K562 cells rescued by LVR-1 MeMe or LVR-2 MeMe. LVR-1 and LVR-2 MeMe represent RNA fragments encompassing MeMe enriched EZH2-interacting RNA motif (Supplementary Fig. 2b) within the LVR-1 and LVR-2 regions (Supplementary Fig. 5a). LEVER KO K562 cells were transduced with empty vector, GFP RNA, LVR-1 MeMe, or LVR-2 MeMe expressing lentivirus and analyzed for ε-globin expression using c RT-qPCR and d western blot. For (c), Data from technical replicates of one biological sample is shown.