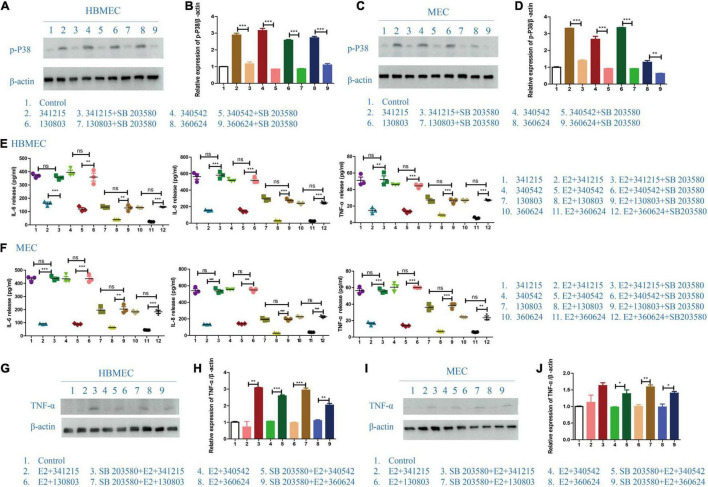
FIGURE 4.
The effect of p38-MAPK signaling pathway on the role of E2 in Neisseria meningitidis-infected cells. (A–D) P38-MAPK signal pathway inhibitor, SB203580, was used in N. meningitidis-infected HBMECs (A) and MECs (C). Proteins were extracted for western blotting analysis. The activation of p-p38 was detected and β-actin was used as the internal control. The changes in protein levels in HBMECs (B) and MECs (D) were analyzed using Image-J software and the gray values were analyzed statistically using GraphPad Prism software. (E,F) HBMECs (E) and MECs (F) were treated with the following three treatments: N. meningitidis infection, E2-N. meningitidis co-stimulation, SB203580-E2-N. meningitidis co-stimulation, and the cell supernatant was collected. ELISA assays were used to detect the levels of IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in the supernatant. (G–J) HBMECs (G) and MECs (I) were divided into three experimental groups as shown. Extracted proteins were subjected to western blotting. The level of TNF-α was detected and β-actin was used as an internal control. The changes of protein levels in both cells (H,J) were analyzed as above. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.