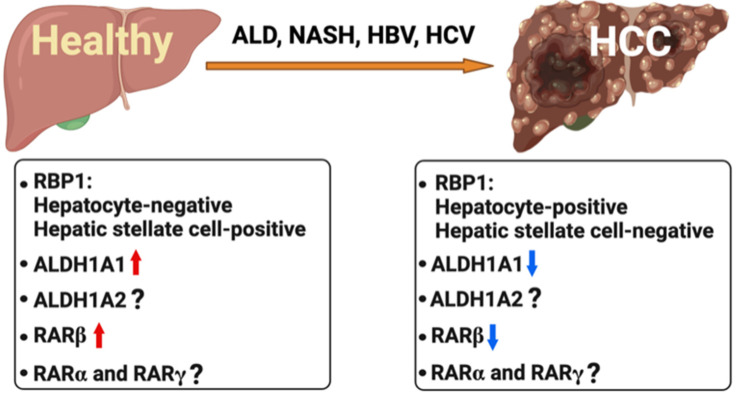
Figure 3.
Retinoids and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and hepatitis virus B and C infection (HBV and HCV) predisposes to the development of HCC. While there is strong evidence that in healthy liver RBP1 (retinol binding protein 1) is expressed predominantly in hepatic stellate cells rather than in the hepatocytes, in HCC RBP1 expression is lost in hepatic stellate cells and observed in hepatocytes. ALDH1A1, which is one of the enzymes responsible for the conversion of retinaldehyde to retinoic acid, is lower (blue downward arrows) in HCC than in healthy liver (red upward arrows). Lower RARβ levels compared with adjacent non-tumor and healthy livers also characterize HCC. There is limited research on RARα and γ in HCC.