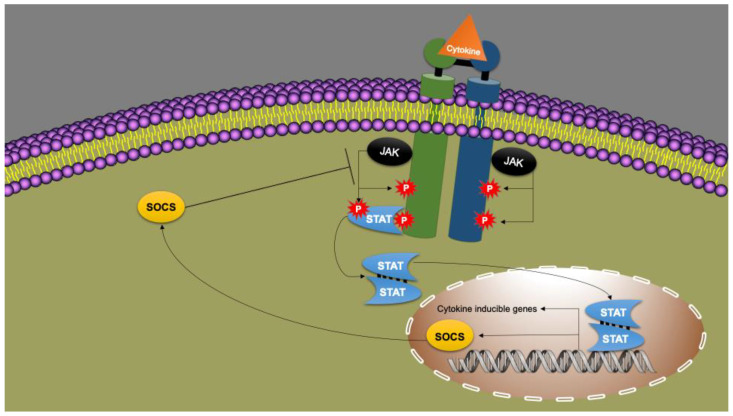
Figure 3.
Cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. A cytokine, such as leptin, binds to its receptor on the plasma membrane. The cytokine receptor is associated with the Janus kinase (JAK; “Just Another Kinase”). JAK phosphorylates two receptor tyrosines, after which JAK is recognized by STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription). Subsequently, STAT is also phosphorylated by JAK. Two phosphorylated STATs form a dimer. The STAT dimer acts as a transcription factor. It binds to the promoter parts of genes affected by that cytokine (“target genes”). These genes are then transcribed into mRNA (DNA to mRNA) and translated into proteins (mRNA to protein). Proteins expressed via this JAK/STAT pathway have functions in proliferation, differentiation, growth and apoptosis. Together they form the products of the “Cytokine Inducible Genes” (CIG). Suppressor Of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS) is also a CIG product. SOCS inhibits the JAK/STAT pathway and thus cytokine signaling. This creates a negative feedback loop. Modified from Morris, Kershaw and Babon [147].