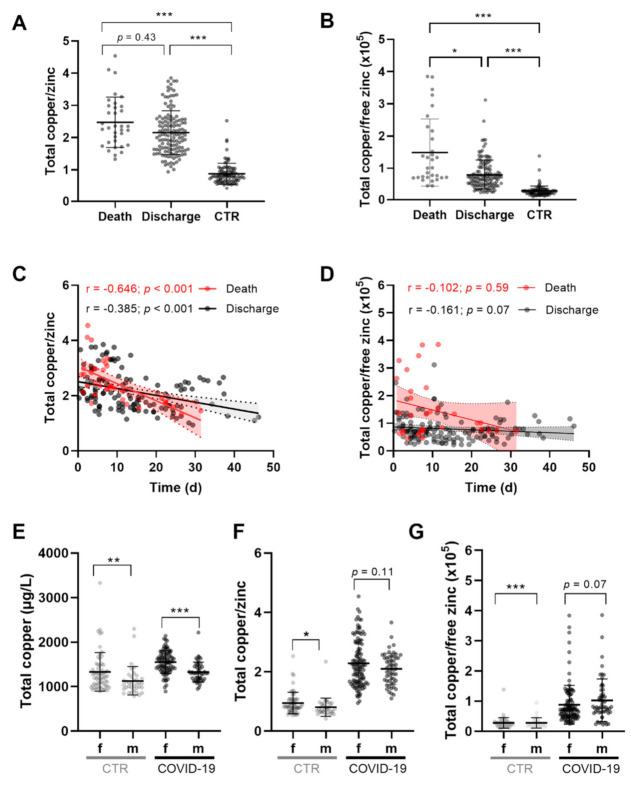
Figure 4.
Analysis of total copper, copper/zinc, and copper/free zinc in serum of patients and controls. Analysis of (A) ratio of total copper and zinc concentrations, (B) total copper and free zinc, (C,D) dynamic changes in COVID-19, and (E–G) comparison of patients with healthy controls (CTR). (A) Total serum copper/zinc concentrations were elevated in COVID-19 patients as compared to controls. (B) Nonsurvivors displayed particularly elevated total copper/free zinc ratio in comparison to those of survivors and controls. (C) Total copper/zinc decreased in serum of COVID-19 patients during hospitalization. (D) Total serum copper/free zinc displayed only slight alterations with time. Consistent sex-specific differences were observed for (E) total serum copper, (F) total copper/zinc, and (G) total copper/free zinc concentrations in control subjects. Significant difference between male and female COVID-19 patients was observed for (E) total copper and (F) total copper/zinc, but not for (G) total copper/free zinc. Differences between two groups were tested with Mann–Whitney U test, and more than two groups were compared with Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison tests (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001). Spearman correlation coefficients (r) are indicated.