Figure 4. C1orf109 and SPATA5 mutant cells exhibit defects in the recycling of RSL24D1.
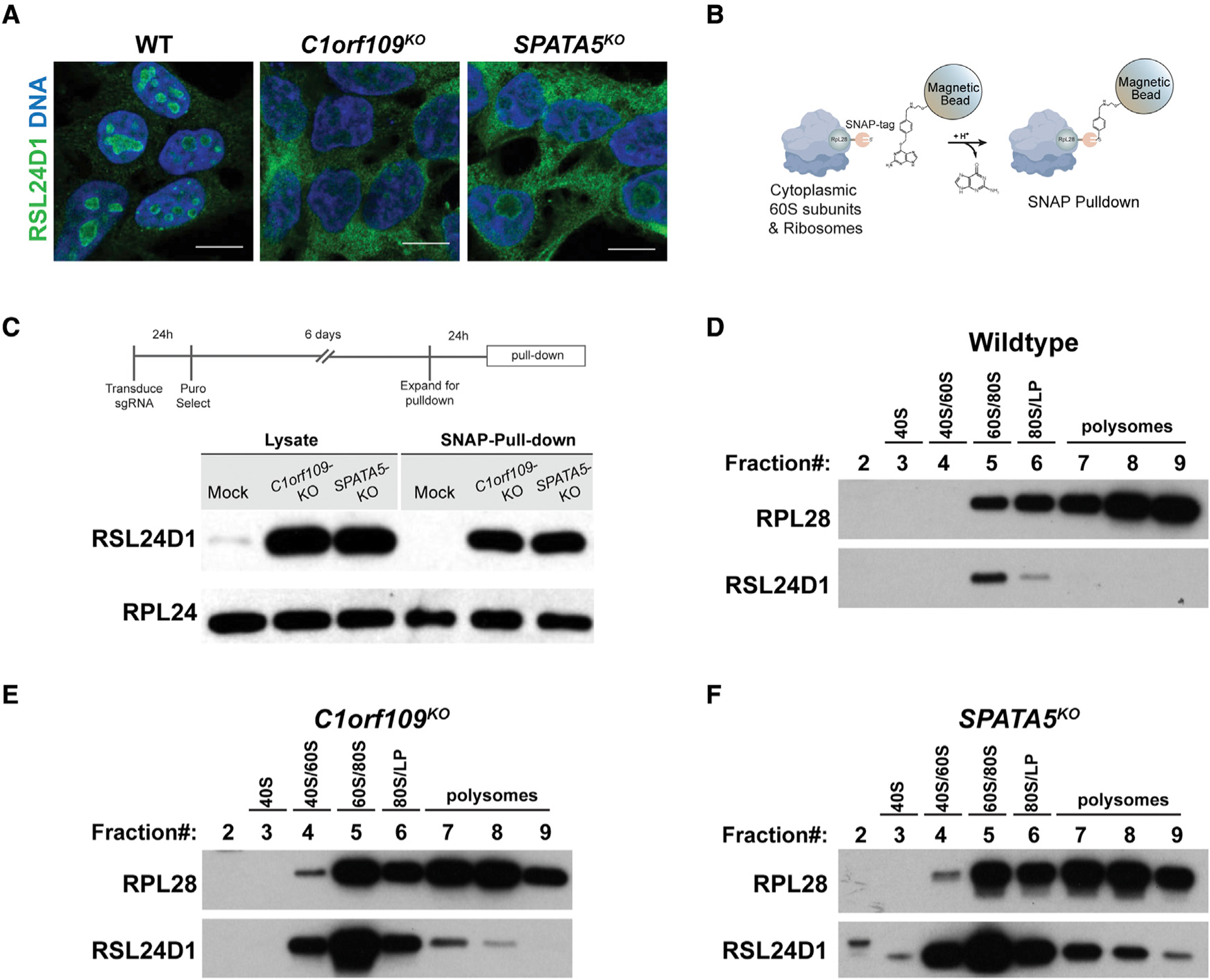
(A) Wild-type (WT) controls and HEK293T cells transduced with sgRNAs targeting C1orf109 and SPATA5 stained for RSL24D1 (green) and DNA (blue). While most RSL24D1 localizes to the nucleoli of control cells, disruption of C1orf109 and SPATA5 results in ectopic localization of RSL24D1 to the cytoplasm. Scale bars, 20 μm.
(B) Overview of SNAP-tagged ribosome pull-down.
(C) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts and Ribo-SNAP pull-down samples probed with either RSL24D1 or RPL24 antibodies. Loss of C1orf109 and SPATA5 results in a dramatic increase in cytoplasmic localization and ribosome associated RSL24D1.
(D) Western blot of sucrose gradient fractions from WT cells probed with antibodies against RPL28 and RSL24D1. Most RSL24D1 was observed in the 60S/80S fraction, with a sharp drop-off in the 80S/light polysome (LP) fraction.
(E) Western blot of sucrose gradient fractions from C1orf109KO cells probed with antibodies against RPL28 and RSL24D1.
(F) Western blot of sucrose gradient fractions from SPATA5KO cells probed with antibodies against RPL28 and RSL24D1.
