Figure 5. Allelic variants of SPATA5 exhibit ribosome assembly defects.
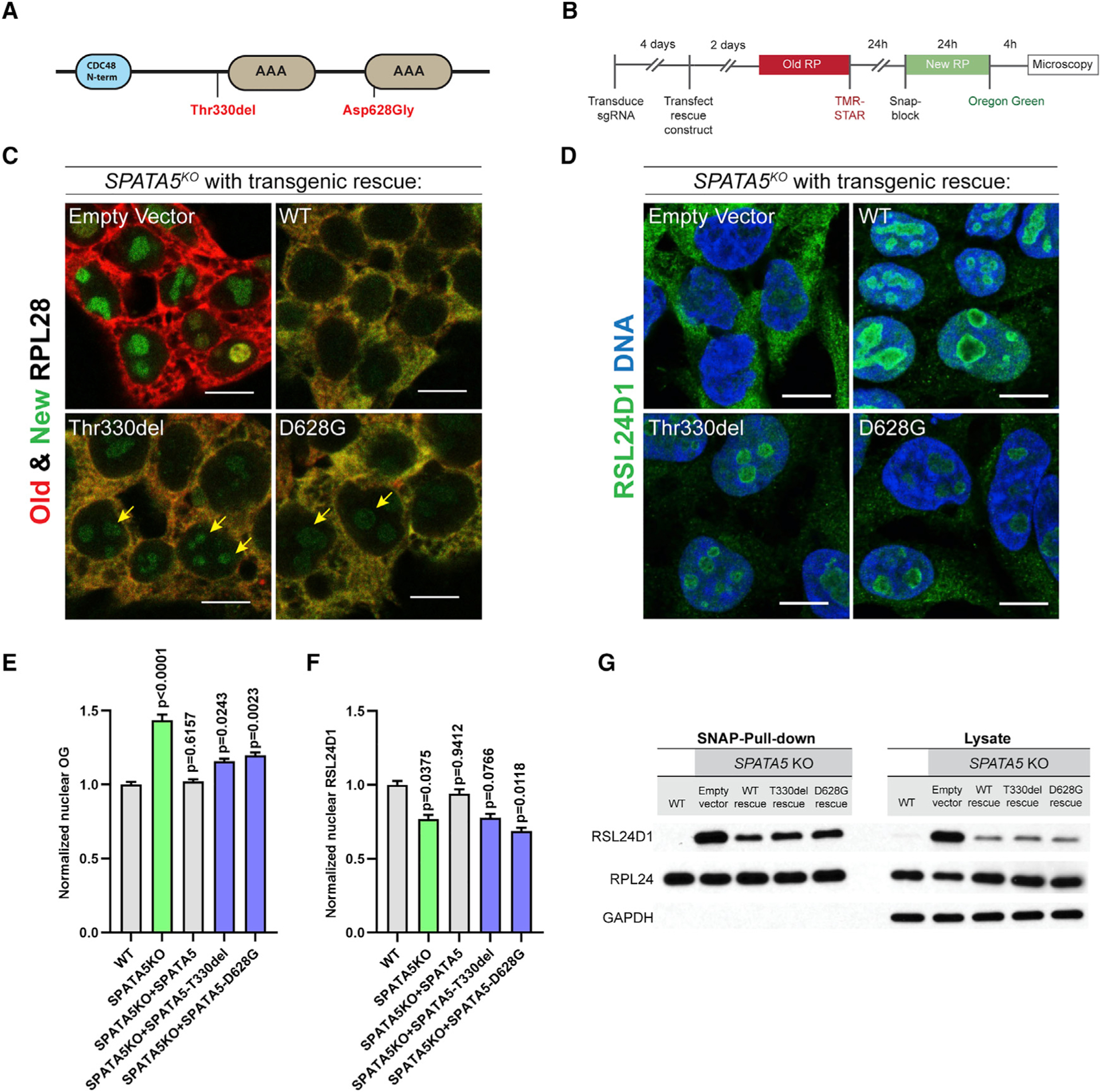
(A) Schematic of SPATA5 domain structure. The two allelic variants indicated in red have been linked with microcephaly, hearing loss, and intellectual disability in humans.
(B) Schematic describing how the labeling of SNAP-tagged RPL28 was conducted.
(C) HEK293T cells were transduced with an sgRNA targeting SPATA5, transfected with plasmids carrying transgenes corresponding to wild-type SPATA5 or the disease-linked (Thr330del and D628G) allelic variants, and old ribosomes were pulse labeled with TMR-Star (red) and new RPL28 proteins were labeled with Oregon green (green), as indicated. The wild-type transgene rescued the RPL28 nucleolar retention phenotype caused by loss of SPATA5, whereas cells expressing the two allelic variants continued to display low levels of newly labeled nucleolar RPL28 after a 4-h chase period (yellow arrows).
(D) Staining cells for RSL24D1 (green) and DNA (blue) showed that, in contrast to wild-type transgenic controls, expression of the Thr330del and D628G variants did not fully rescue the localization defects of RSL24D1 in SPATA5 mutant cells.
(E) Quantification of Oregon green (OG)-labeled new SNAP-tagged RPL28 within nuclei in the indicated genetic backgrounds. n = 3 biological replicates.
(F) Quantification of nuclear RSL24D1 staining in the indicated genetic backgrounds. n = 3 biological replicates. Statistical comparisons in (E and F) are between wild-type cells and cells with each of the indicated rescuing transgenes. Mean ± SEM is shown. p values were calculated by nested one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
(G) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts and Ribo-SNAP pull-down samples probed with RSL24D1 and RPL24 antibodies. Wild-type transgenes could partially rescue the increase of cytoplasmic RSL24D1 and its aberrant prolonged association with the 60S subunit in SPATA5 mutant cells. By contrast, the amount of cytoplasmic and ribosome bound RSL24D1 were modestly elevated upon expression of the Thr330del and D628G allelic variants relative to the wild-type control. Scale bars, 10 μm.
