Figure 6. SPATA5 and C1ORF109 interact with CINP and SPATA5L1.
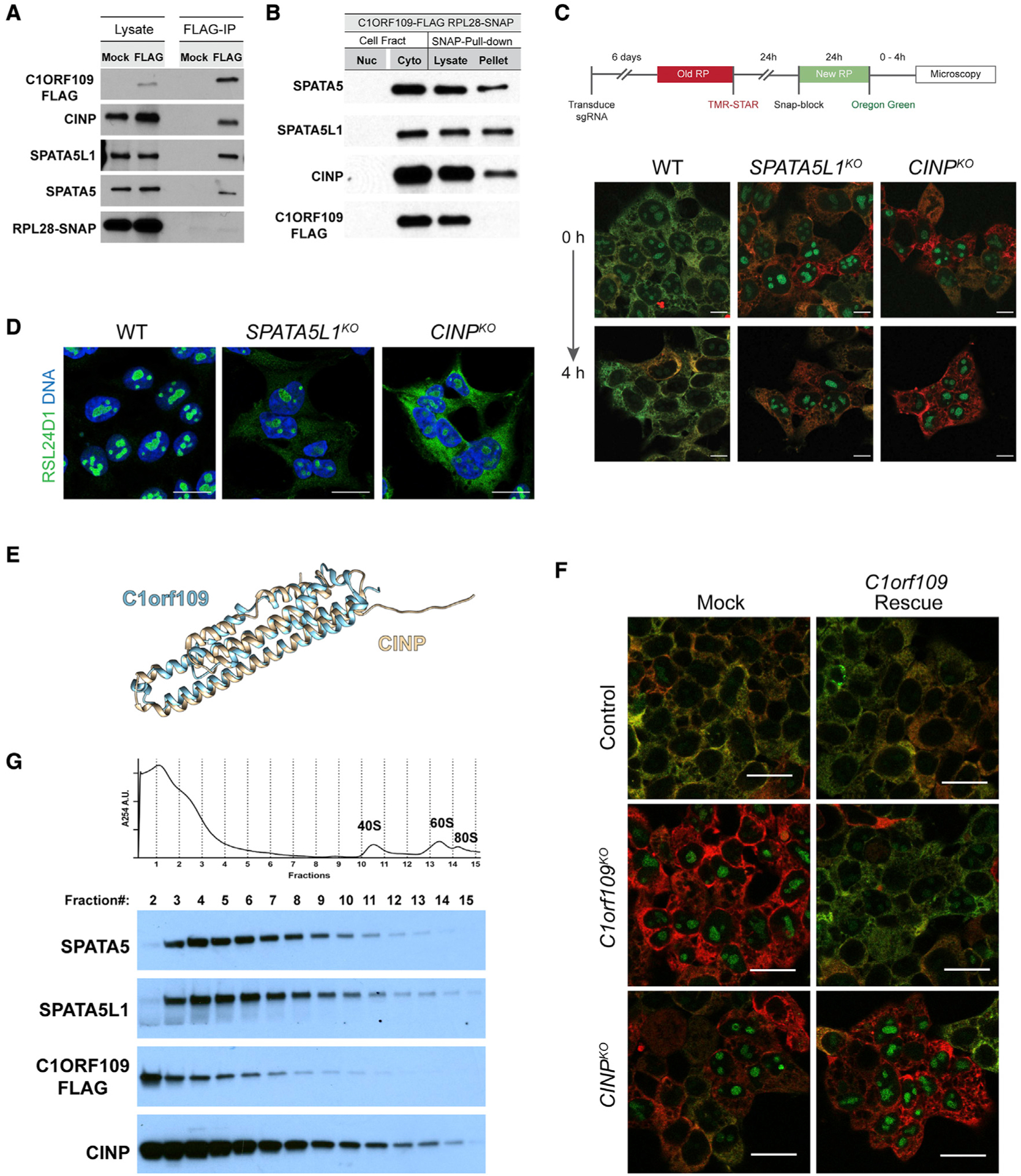
(A) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged C1ORF109 from HEK293T cell extracts crosslinked with DSP reveals that C1ORF109 physically interacts with SPATA5, SPATA5L1, and CINP, but not with RPL28.
(B) Pull-down of SNAP-tagged RPL28 shows that SPATA5, SPATA5L1, and CINP interact with ribosomes, but C1ORF109 does not.
(C) Knockout of SPATA5L1 or CINP leads to defects in the trafficking of newly labeled RPL28 from the nucleolus to the cytoplasm.
(D) Control, SPATA5L1KO, and C1orf109KO cells stained for RSL24D1 (green) and DNA (blue).
(E) Matchmaker alignment of CINP and C1ORF109 AlphaFold predicted structures.
(F) Control, CINPKO, and C1orf109KO cells transfected with a control or C1orf109 rescue construct stained for old and new ribosomes.
(G) Cytoplasmic lysates from C1ORF109–3xFLAG expressing cells subjected to sucrose gradient fractionation and probed for SPATA5, SPATA5L1, C1ORF109, and CINP.
