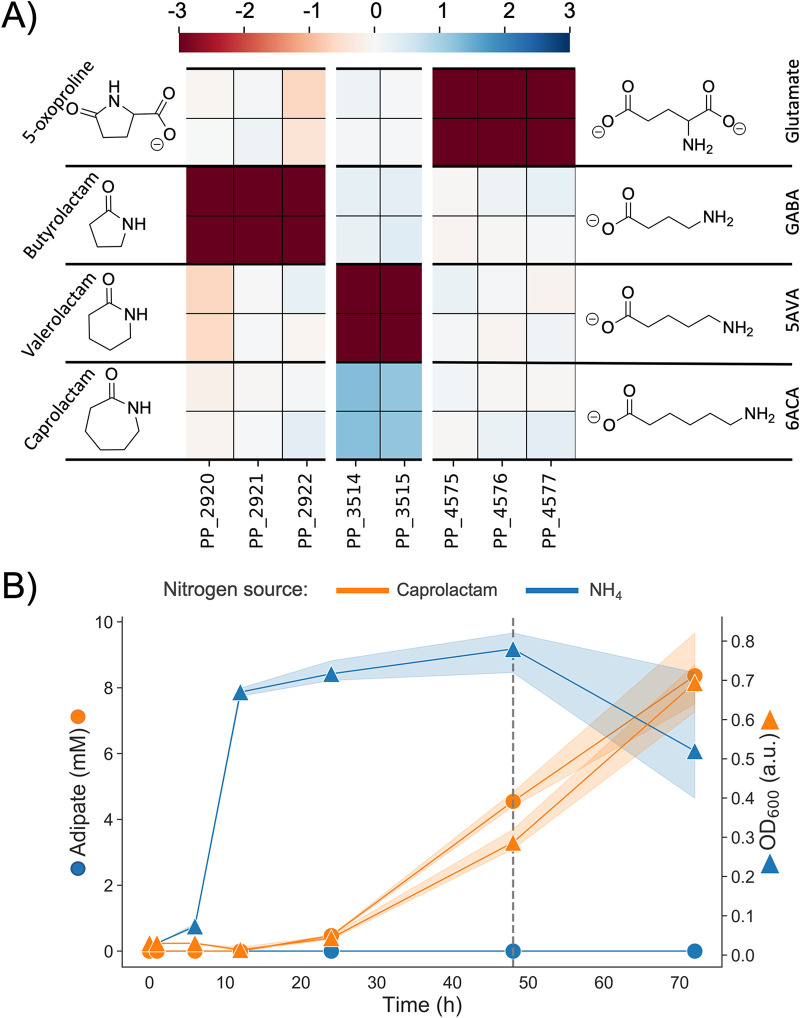
FIG 6.
(A) Heatmap with fitness scores (n = 2) of genes putatively involved in the hydrolysis of caprolactam, valerolactam, butyrolactam, and 5-oxoproline in P. putida KT2440. (B) LC-MS analysis of caprolactam degradation in P. putida KT2440. Wild-type cells were grown in MOPS minimal media with ammonium (blue) and caprolactam (orange) as the sole source of nitrogen. Shown is the OD (squares) and concentration of adipate in the supernatant (circles) over a time course of 72 h. The dashed line marks the time point at which caprolactam was no longer detected in the media.