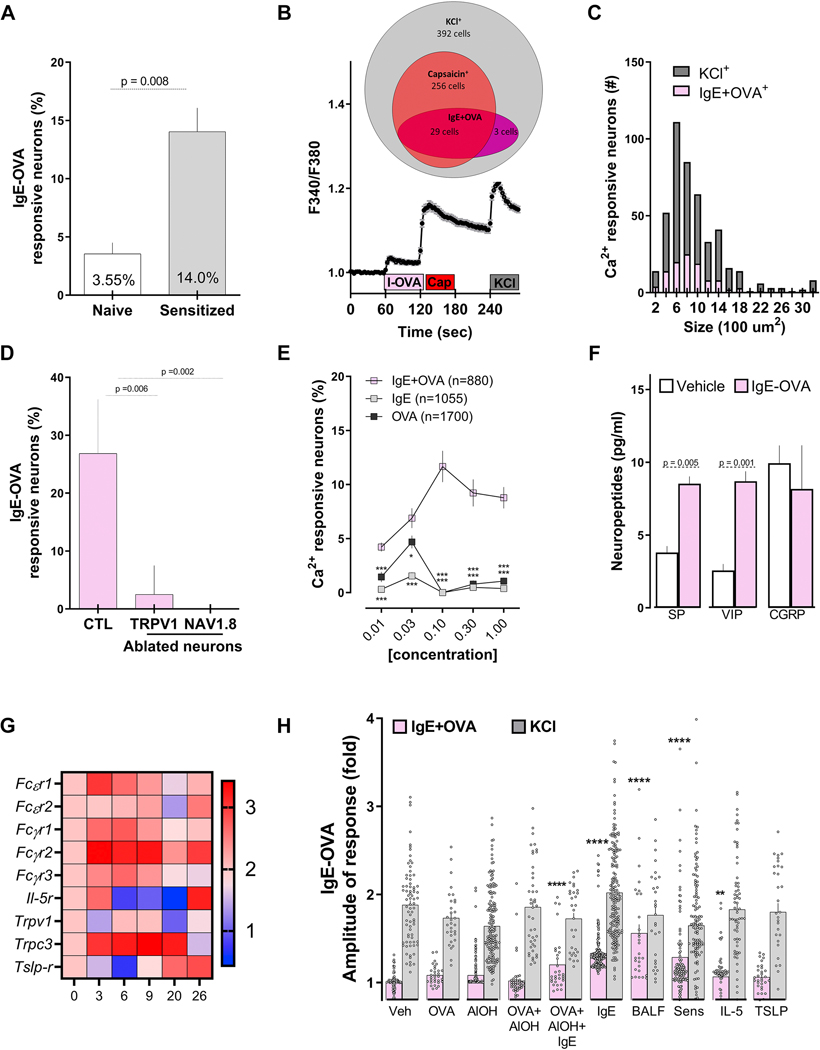
Figure 3: IgE-Ovalbumin complex evokes calcium flux in vagal nociceptors.
Ultra-pure ovalbumin (1%), when complexed with mouse recombinant immunoglobulin E (IgE, 0.001%), triggered larger calcium transients in cultured JNC neurons obtained from allergen-sensitized (day 14) than from naïve mice (A). Shown is an example of the response evoked in capsaicin-sensitive neurons (B). IgE-OVA-induced calcium influx was mostly observed in small-sized neurons (C) and capsaicin-sensitive neurons and absent in cultured neurons obtained from allergen-sensitized (day 14) TRPV1 (TRPV1creDTAfl/wt) or NaV1.8 (NaV1.8creDTAfl/wt) nociceptor ablated mice. (D). The IgE-OVA complex dose-dependently evoked a calcium response greater than that for IgE or OVA alone (E) and triggered the release of substance P (SP) and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP; F). Capsaicin- responsive neurons were picked at various time points of the allergy-induction protocol and analyzed by single-cell qPCR. Allergen sensitization transiently drove the expression of FcsR1, which peaked on day 3 (G). Compared with naïve vagal neurons, we found an increased number of immune complex-responsive neurons in cells pre-treated (24h) with IgE, OVA+AlOH+IgE, IL-5, or asthmatic BALF or harvested from allergen-sensitized (day 14) mice (H). Mean ± S.E.M; Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test (A, D, F); two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test (H), one-way ANOVA post-hoc Bonferroni (E); n = 3–8 animals/group, 2–3 cohorts. In (B), IgE-OVA (1%+0.001%; 60–75 sec) is represented by the pink box, capsaicin (1 jM; 120–135 sec) is represented by the red box, and the gray box represents KCl (40 mM; 240–255 sec). Relative gene expression was ratioed over day 0, multiplied by 1000, and the Log10 of these values were presented as a heatmap (G).