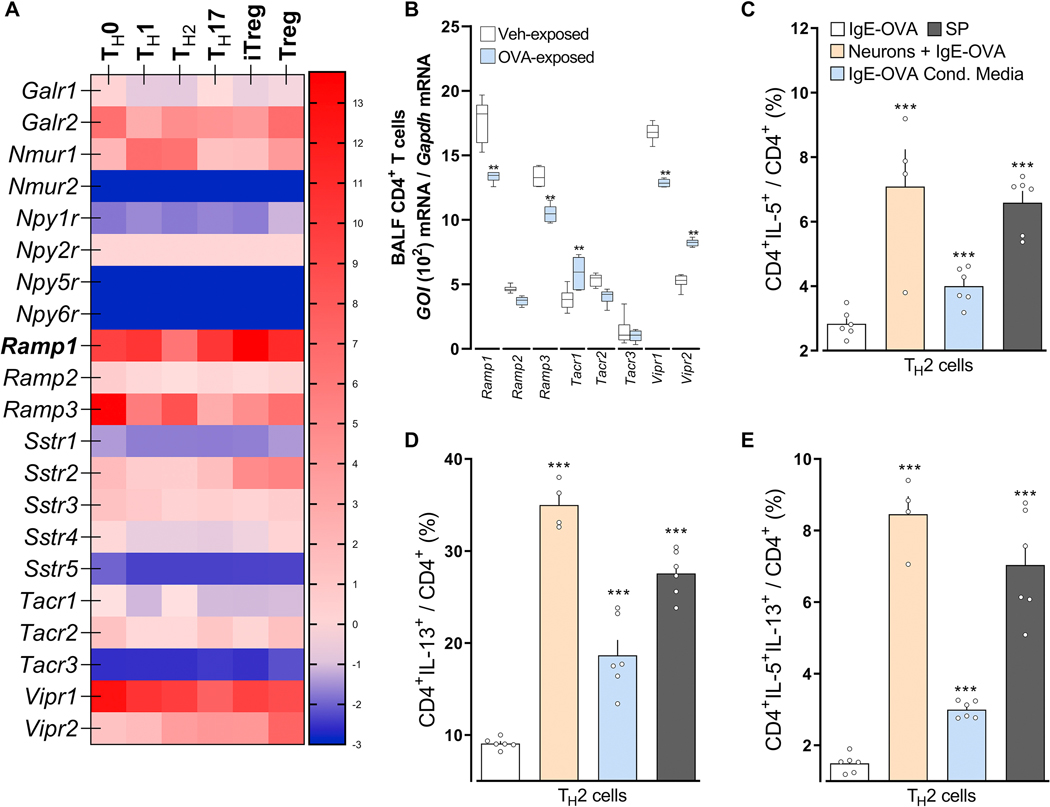
Figure 5: Following allergen sensing, FctR1+ nociceptor neurons drive TH2 cell polarization.
In comparison to naïve, TH1, TH17, iTreg and Treg (A), or naïve CD4 T cells (B), TH2 cells (A; In-silico analysis of Immgen’s RNA sequencing data) or BALF CD4 T cells harvested from OVA-challenged mice (day 15; B) showed increased Tacrl transcript expression (A, B). Purified naïve CD4 spleen cells were polarized into TH2 cells and then either: co-cultured with allergen-sensitized mice JNC neurons (beige bar), stimulated with conditioned media harvested from IC-stimulated allergen-sensitized JNC neurons (blue bar) or with Substance P (C-E; gray bar). In comparison to IgE-OVA-stimulated TH2 cells, TH2 cells co-cultured with neurons then stimulated with neuron-conditioned media or Substance P, showed increased levels of IL-5+ (C), IL-13+ (D), and IL-5+IL-13+ (E). Mean ± S.E.M; Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test (B-E). Transcript expression are shown as DESeq2 normalized counts (A). Stimulation and co-culture were done in the presence of a cocktail of protease inhibitors (1/1000; C-E); n = 5–6 animals/group, 2 cohorts.