Fig. 1.
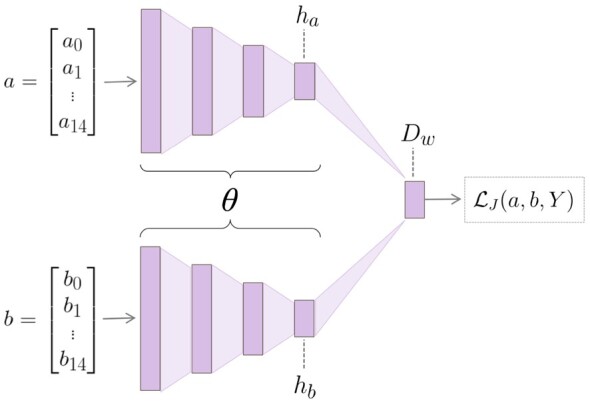
Siamese neural network architecture, composed of twin CNNs. The twin networks are joined at the final layer. The vectors a and b represent a pair of motifs from the training set, while ha and hb represent the respective hidden layers output by either CNN. The difference between the hidden layers is calculated to obtain the distance layer, Dw. Dw is input into the loss along with Y, a variable indicating the dissimilarity, regarding kinase interactions, between a and b. After training is complete, the so-called ‘twin’ architecture is no longer necessary; each motif is input into a single twin and the output of the embedding layer gives the resultant representation of the given motif
