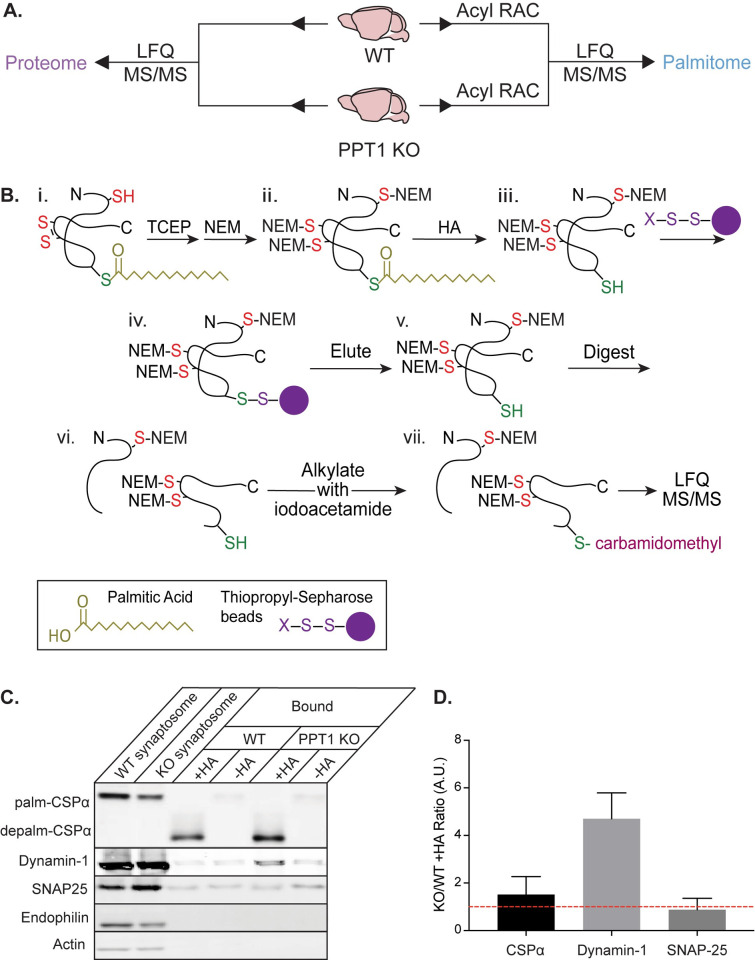
Fig 1. Generation of the proteome and palmitome from WT and PPT1 KO brains.
(A) Proteins were isolated from WT and PPT1 KO whole brains or synaptosomes for proteomic analysis by LFQ-MS to identify overall protein expression (proteome; left) or following Acyl RAC to identify palmitoylated proteins (palmitome; right). (B) Schematic of Acyl RAC. (i) Disulfide bonds were reduced with TCEP and residual thiol groups were blocked with NEM. (ii) Palmitate groups were hydrolyzed with HA, leaving behind an unblocked free thiol. (iii) Free thiols were bound to thiopropyl sepharose beads, allowing for isolation of palmitoylated proteins. These proteins were then (iv) eluted from beads with DTT, (v) digested, and (vi) alkylated with iodoacetamide, followed by (vii) LFQ-MS/MS analysis. (C) Pull-down and immunoblotting of palmitoylated proteins. Addition of HA allowed CSPα, dynamin-1, and SNAP-25, all of which are palmitoylated proteins, to be pulled down on thiopropyl sepharose beads, but not endophilin or actin, which are not palmitoylated. Note that addition of HA removes palmitate and causes a molecular weight shift of palmitoylated CSPα to depalmitoylated CSPα. (D) Quantification of western blot +HA band intensity (A.U), plotted as a ratio of KO/WT (S1 Data). CSPα is a known PPT1 substrate and shows elevated palmitoylation in KO/WT, while SNAP-25 does not (n = 3 to 9 experiments). Acyl RAC, Acyl Resin-Assisted Capture; HA, hydroxylamine; KO, knockout; LFQ-MS, Label-Free Quantification Mass Spectrometry; NEM, N-ethylmaleimide; PPT1, palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1; TCEP, tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine; WT, wild-type.