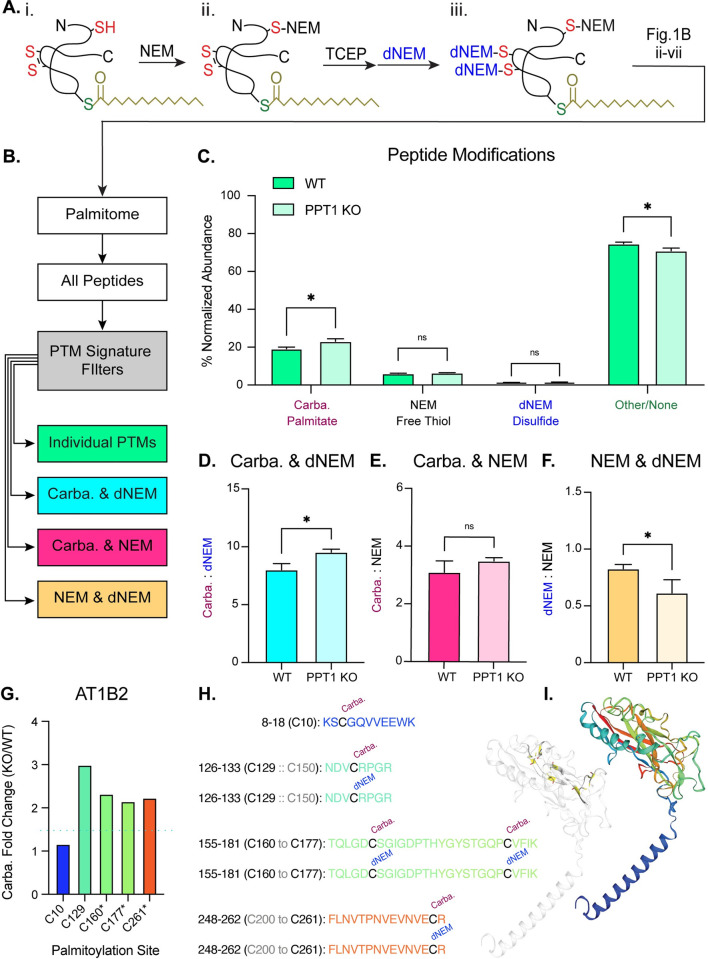
Fig 5. PPT1-mediated depalmitoylation facilitates disulfide bond formation.
(A) Schematic of modified Acyl RAC. (i) Free thiols were blocked with NEM prior to reduction of disulfide bonds with TCEP. (ii) Free thiols generated by TCEP treatment were modified with heavy-labeled NEM (dNEM). iii. Acyl RAC was then conducted as previously described (Fig 1Bii–iv). (B) Pipeline for PTM analysis of Acyl RAC peptide data. Peptides were aggregated from 3 independent proteomic screens with 3 biological replicates. All peptides were filtered by individual PTMs or by coincidence signatures where 2 distinct PTMs were found to modify the same cysteine residue. (C) Global distribution of modified peptides. Bars represent percent (%) average normalized abundance of the different peptide classes. The value of each replicate is calculated as the summed abundance of peptides with the given PTM normalized to the total abundance for all detected peptides (S1 Data). Cysteine residues with PTMs are interpreted as follows: carbamidomethyl (carba.) = palmitate, NEM = free thiol, dNEM = disulfide bond, other or no moieties (Other/None). (D–F) Ratios of PTM normalized abundance for peptides where 2 PTMs are found to modify the same cysteine residue. The value of each replicate is calculated as the summed abundance of peptides with the first PTM divided by the summed normalized abundance of peptides with the second PTM (mean ± SD; * p < 0.05, unpaired, 2-tailed t test; S1 Data). (G) Peptide analysis of a high-confidence PPT1 substrate, Sodium/Potassium transporting ATPase subunit β1 (AT1B2). Normalized abundance fold change (PPT1 KO/WT) of carbamidomethyl AT1B2 peptides (1.5-fold change indicated by blue dashed line). Palmitoylated cysteine sites marked with an asterisk (*) were confirmed to be PPT1 substrates in the validation screen. There is a persistence of palmitates on cysteines that normally participate in disulfide bonds in PPT1 KO (C129, C160, C177, and C261; S5 Table), while C10, which is not predicted to form a disulfide linkage, appears unchanged (S1 Data). (H) Detected AT1B2 peptides are indicated. For those sequences with cysteines predicted to form disulfide bonds, carba. and dNEM moieties were found to modify that cysteine residue. (I) Ribbon structure of AT1B2 (SWISS-MODEL; P14231) with disulfide bonds highlighted. Bar graph and peptide sequences are color coded according to location in the ribbon structure. Acyl RAC, Acyl Resin-Assisted Capture; dNEM, d5-N-ethylmaleimide; KO, knockout; NEM, N-ethylmaleimide; PPT1, palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1; PTM, posttranslational modification; TCEP, tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine; WT, wild-type.