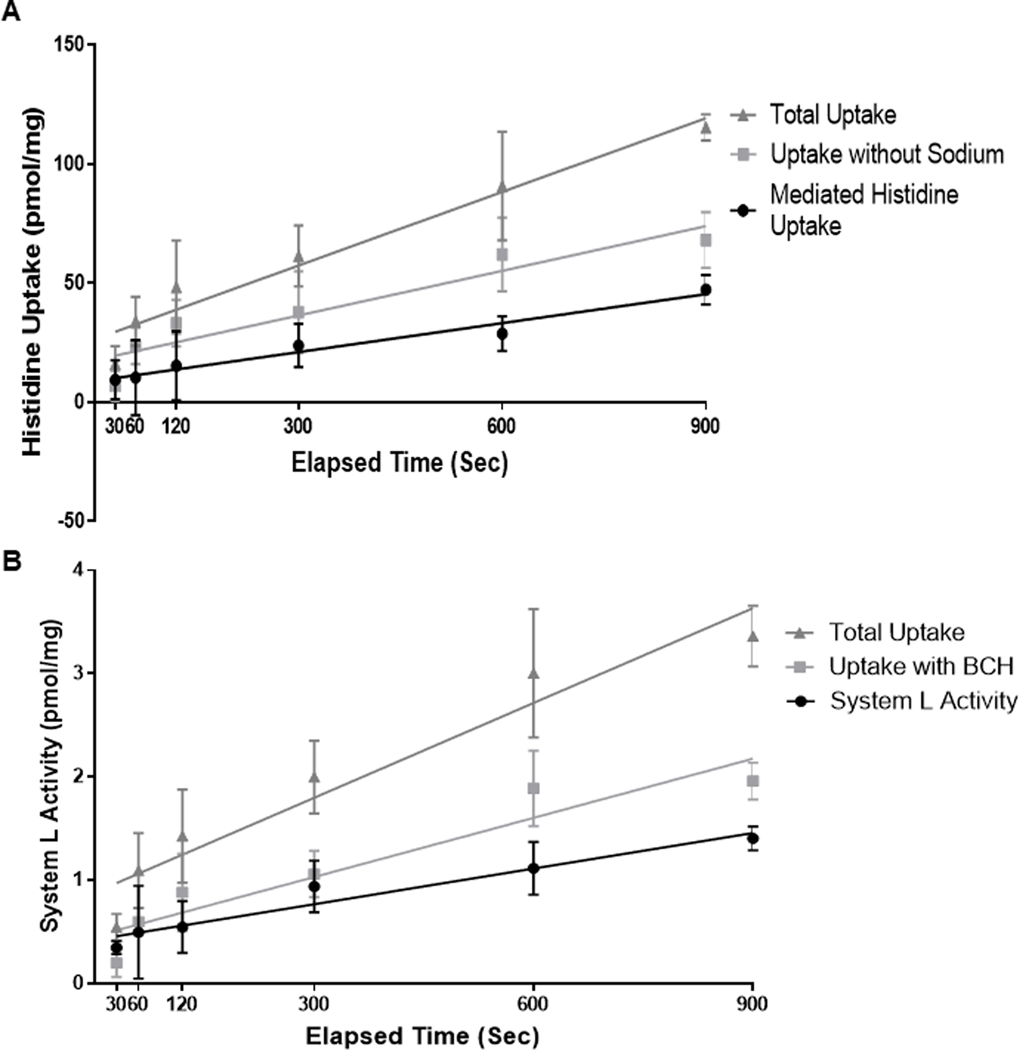
Figure 2. Time dependence of histidine uptake and system L activity (A).
(A) (▲) = Total histidine uptake; (■) = Sodium-independent histidine uptake plus unspecific binding; (•) = Mediated histidine uptake. (B) (▲) = Total leucine uptake; (■) = Uptake in the presence of BCH (2-amino-2-norbornanecarboxylic acid, an amino acid analogue exclusively transported by system L) representing leucine uptake not mediated by system L plus unspecific binding. (•) = BCH-inhibitable leucine uptake (system L activity). N=4 for 30,60,120, and 300 second time points or n=2 for 600 and 900 second time points. Histidine and leucine uptake were linear during the first 900 seconds.