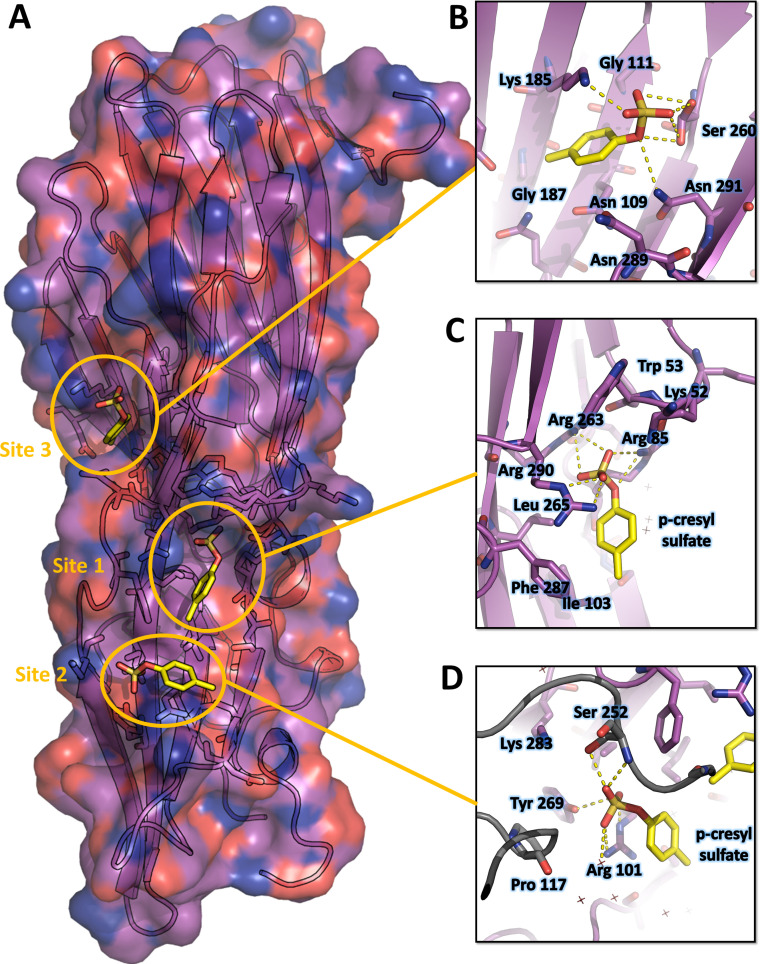
Figure 3. Crystal structure of LukE in complex with p-cresyl sulfate.
(A) Overview of the asymmetric unit of the crystal. Protein is shown in cartoon representation and colored magenta. The p-cresol sulfate molecules are shown in yellow sticks with surrounding protein residue sidechains in magenta lines (B–D). Close ups of the sulfotyrosine binding sites. The color code is the same as in (A) with p-cresol sulfate molecules and protein sidechains shown in sticks. Polar contacts between ligand and protein are shown as yellow dashed lines. In (D), protein residues from an interacting symmetry related molecule are shown in gray cartoon and sticks.