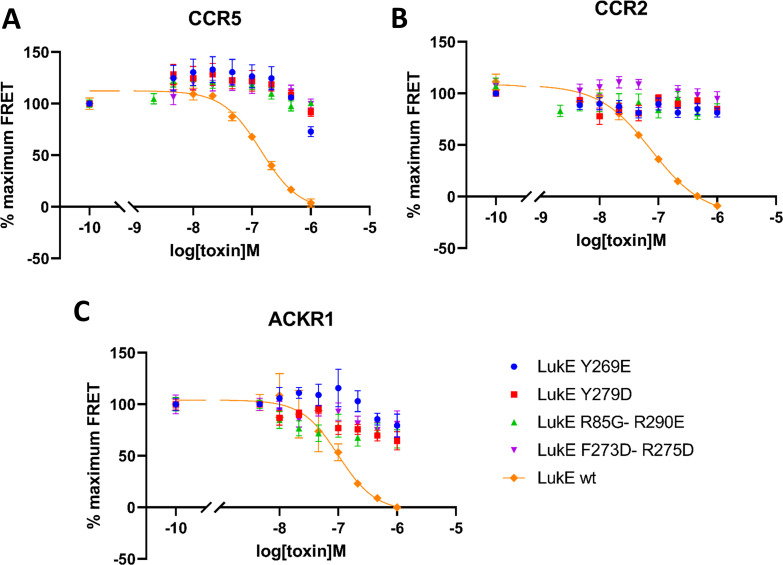
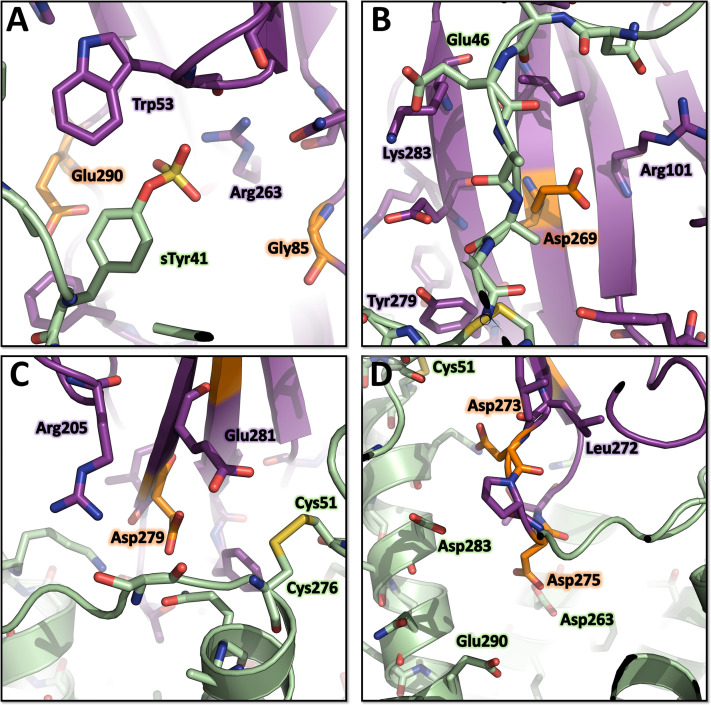
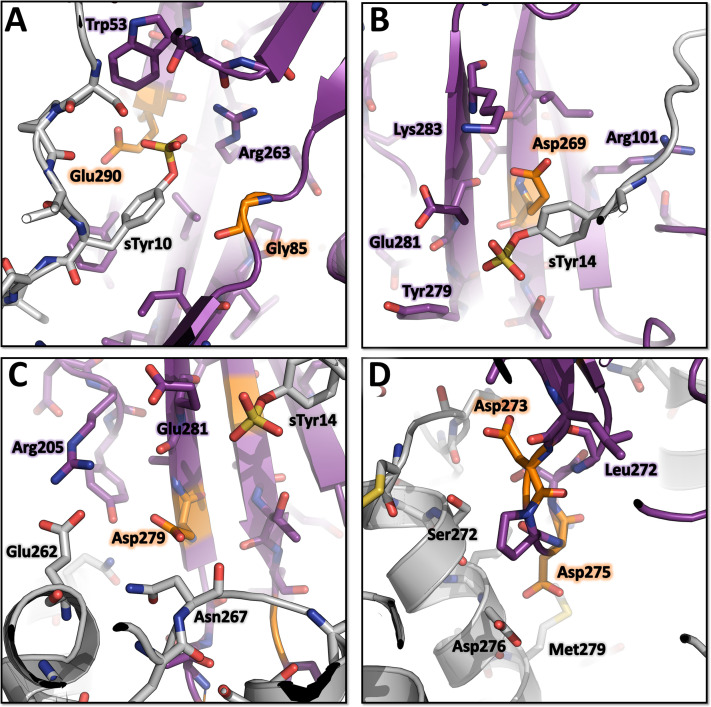
Figure 8. Effects of R85G + R290 E, Y269D, Y279D, and F273D + R275 D mutations on the binding of LukE in live cells as determined by competition time-resolved fluorescence energy transfer (TR-FRET).
5 nM tracer ligands, CCL5-d2 for CCR5 (A) and ACKR1 (C) and CCL2-d2 for CCR2 (B), were used to determine TR-FRET at their respective receptors in the presence of LukE mutants or wild-type LukE. IC50 values were undetermined for LukE mutants due to loss of binding. Data shown is mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate.