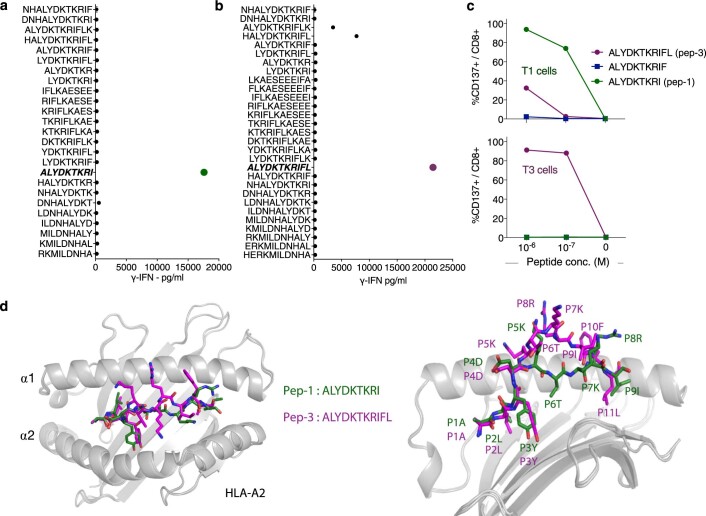
Extended Data Fig. 3. T1 and T3 cell activation in response to length variants of cognate peptides and model of structural conformation of TdT peptides in the HLA-A2 peptide-binding groove.
(a,b) IFN-γ production by the T1 (a) and T3 (b) cells after co-culture with target cells loaded with indicated peptides. 9-mer and 11-mer peptides were included that contained amino acids upstream or downstream of the wild type peptide-1 and -3 in the TdT protein sequence. In addition, 8 to 12 amino acid long peptides were included that contained parts or all of peptide-1 and -3. One replicate per condition. (c) Percentage of CD137+ events among T1 and T3 cells after co-culture with EBV-LCLs loaded with indicated concentrations of cognate, or non-cognate, peptide-1 (ALYDKTKRI) or -3 (ALYDKTKRIFL). Reactivity to a 10-mer peptide (ALYDKTKRIF) is also shown. One replicate per condition. Data shown are from one experiment representative of 2 performed. (d) Overlaid structural conformations of peptide-1 and -3 bound to the HLA-A2 molecule shown from top (left) and side view (right). HLA-A2 is shown as cartoon in gray. Peptide-1 (green) and peptide-3 (purple) are shown as stick. Individual amino acids are labeled as a number in the corresponding peptide followed by their symbol. The modeled peptide-1 on HLA-A2 displays a flattened conformation, and amino acids at position (P)4, P5, P7 and P8 are facing up for potential TCR engagement. The model is supported by the mimotope reactivity pattern, as T1 was intolerant to mutations in P4, P5, P7 and P8. Although P3Y is not facing upward for TCR contact, it is likely to stabilize the peptide-MHC interaction and is thus sensitive to mutations. The P4, P5, P7 and P8 as core TCR contact residues are salient features for 9-mer peptides presented by HLA-A2. Peptide-3 displays a bulged conformation, in which P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9 residues are facing upwards for TCR contact. P4D and P5K are less important for TCR engagement than for peptide-1, as P4D can be substituted by almost any amino acid and P5K can be substituted by amino acids with long or bulky side chains. P6-P10 are potentially important for TCR contact, and as shown in our cross-reactivity assay, T3 was less tolerant for substitutions of these amino acids.